IL1beta- and LPS-induced serotonin secretion is increased in EC cells derived from Crohn's disease
- PMID: 19019013
- PMCID: PMC4040949
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2008.01210.x
IL1beta- and LPS-induced serotonin secretion is increased in EC cells derived from Crohn's disease
Abstract
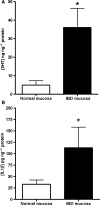
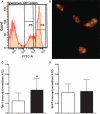
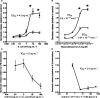
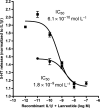
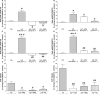
Gut mucosal enterochromaffin (EC) cells are regarded as key regulators of intestinal motility and fluid secretion via secretion of serotonin (5HT), are increased in numbers in mucosal inflammation and located in close proximity to immune cells. We examined whether interleukin (IL)1beta and Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced EC cell 5HT release through Toll-like/IL-1 (TIL) receptor activation, nuclear factor kappa B (NFkappaB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation and evaluated whether somatostatin could inhibit this phenomenon. Pure (>98%) human intestinal EC cells were isolated by fluorescent activated cell sorting from preparations of normal (n = 5) and Crohn's colitis (n = 6) mucosa. 5HT release was measured (ELISA), and NFkappaB and ERK phosphorylation quantitated (ELISA) in response to IL1beta and LPS. 5HT secretion was increased by both E. coli LPS (EC(50) = 5 ng mL(-1)) and IL1beta (EC(50) = 0.05 pmol L(-1)) >2-fold (P < 0.05) in Crohn's EC cells compared with normal EC cells. Secretion was reversible by the TLR4 antagonist, E. coli K12 LPS (IC(50) = 12 ng mL(-1)) and the IL1beta receptor antagonist (ILRA; IC(50) = 3.4 ng mL(-1)). IL1beta caused significant (P < 0.05) NFkappaB and MAPK phosphorylation (40-55%). The somatostatin analogue, lanreotide inhibited IL1beta-stimulated secretion in Crohn's (IC(50) = 0.61 nmol L(-1)) and normal EC cells (IC(50) = 1.8 nmol L(-1)). Interleukins (IL1beta) and bacterial products (E. coli LPS) stimulated 5HT secretion from Crohn's EC cells via TIL receptor activation (TLR4 and IL1beta). Immune-mediated alterations in EC cell secretion of 5HT may represent a component of the pathogenesis of abnormal bowel function in Crohn's disease. Inhibition of EC cell-mediated 5HT secretion may be an alternative therapeutic strategy in the amelioration of inflammatory bowel disease symptomatology.
Figures
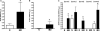
Similar articles
-
The role of mechanical forces and adenosine in the regulation of intestinal enterochromaffin cell serotonin secretion.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Feb 1;302(3):G397-405. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00087.2011. Epub 2011 Oct 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22038827 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide attenuates LPS-induced cellular injury in human fetal lung fibroblasts via inhibiting MAPK and NF-κB pathway activation.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Aug;14(2):1785-90. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5400. Epub 2016 Jun 14. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27314600
-
Aloe vera downregulates LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine production and expression of NLRP3 inflammasome in human macrophages.Mol Immunol. 2013 Dec;56(4):471-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.05.005. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23911403
-
Induction of in vitro reprogramming by Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 and TLR4 agonists in murine macrophages: effects of TLR "homotolerance" versus "heterotolerance" on NF-kappa B signaling pathway components.J Immunol. 2003 Jan 1;170(1):508-19. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.1.508. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12496438
-
Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans lipopolysaccharide induces interleukin-6 expression through multiple mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in periodontal ligament fibroblasts.Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2006 Dec;21(6):392-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302X.2006.00314.x. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17064398
Cited by
-
The Role of 5-HT Dysregulation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2013 Apr;9(4):259-61. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2013. PMID: 24711774 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pathophysiologic Role of Neurotransmitters in Digestive Diseases.Front Physiol. 2021 Jun 14;12:567650. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.567650. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34194334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain-Gut-Microbiome Interactions and Intermittent Fasting in Obesity.Nutrients. 2021 Feb 10;13(2):584. doi: 10.3390/nu13020584. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33578763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding the Molecular and Mutational Ambiguities of Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasm Pathobiology.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Jan 12;1(2):131-153. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2014.12.008. eCollection 2015 Mar. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 28210673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enteroendocrine cells-sensory sentinels of the intestinal environment and orchestrators of mucosal immunity.Mucosal Immunol. 2018 Jan;11(1):3-20. doi: 10.1038/mi.2017.73. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Mucosal Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28853441 Review.
References
-
- Crowell MD, Shetzline MA, Moses PL, Mawe GM, Talley NJ. Enterochromaffin cells and 5-HT signaling in the pathophysiology of disorders of gastrointestinal function. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2004;5:55–60. - PubMed
-
- Thompson A, Keelman M, Thiesen A, Clandinin M, Ropeleski M, Wild G. Small bowel review: normal physiology part 2. Dig Dis Sci. 2001;46:2588–607. - PubMed
-
- Yang GB, Lackner AA. Proximity between 5-HT secreting enteroendocrine cells and lymphocytes in the gut mucosa of rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta) is suggestive of a role for enterochromaffin cell 5-HT in mucosal immunity. J Neuroimmunol. 2004;146:46–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

