Induction of lymphotoxin-alpha by interleukin-12 p40 homodimer, the so-called biologically inactive molecule, but not IL-12 p70
- PMID: 19019087
- PMCID: PMC2712100
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02985.x
Induction of lymphotoxin-alpha by interleukin-12 p40 homodimer, the so-called biologically inactive molecule, but not IL-12 p70
Abstract
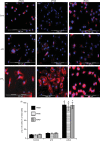
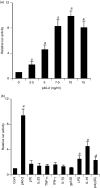
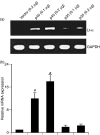
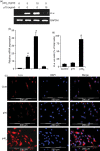
Interleukin-12 (IL-12) p70 (p40:p35) is a bioactive cytokine and its biological functions are becoming clear. On the other hand, the IL-12 p40 homodimer (p40(2)) was considered an inactive or inhibitory molecule and its functions are poorly understood. It has been reported that increased expression of lymphotoxin-alpha (Lt-alpha) in the central nervous system as well as in peripheral immune cells is associated with multiple sclerosis and experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Here we describe that p40(2) induces the expression of Lt-alpha in primary mouse and human microglia, BV-2 microglial cells, splenic macrophages, RAW 264.7 cells and splenic T cells. Interestingly, IL-12 p70 was either unable to induce Lt-alpha or was a very weak inducer of Lt-alpha in these cell types. Consistently, p40(2), but not p70, induced Lt-alpha promoter-driven luciferase activity in microglial cells. Among various stimuli tested, p40(2) emerged as the most potent followed by IL-16, lipopolyaccharide and double-stranded RNA in inducing the activation of Lt-alpha promoter in microglial cells. Furthermore, an increase in Lt-alpha messenger RNA expression by overexpression of p40, but not p35, complementary DNA and induction of Lt-alpha expression by p40(2) in microglia isolated from IL-12p35(-/-) mice confirm that p40, but not p35, is responsible for the induction of Lt-alpha. Finally, by using primary microglia from IUL-12 receptor beta1 deficient (IL-12Rbeta1(-/-)) and IL-12Rbeta2(-/-) mice, we demonstrate that p40(2) induced the expression of Lt-alpha in microglia and macrophages via IL-12Rbeta1, but not IL-12Rbeta2. These studies delineate a novel biological function of p40(2) that is absent in IL-12.
Figures



References
-
- Crowe PD, VanArsdale TL, Walter BN, et al. A lymphotoxin-beta-specific receptor. Science. 1994;264:707–10. - PubMed
-
- Cannella B, Sizing ID, Benjamin CD, Browning JL, Raine CS. Antibodies to lymphotoxin alpha (LT alpha) and LT beta recognize different glial cell types in the central nervous system. J Neuroimmunol. 1997;78:172–9. - PubMed
-
- Matusevicius D, Navikas V, Soderstrom M, Xiao BG, Haglund M, Fredrikson S, Link H. Multiple sclerosis: the proinflammatory cytokines lymphotoxin-alpha and tumour necrosis factor-alpha are upregulated in cerebrospinal fluid mononuclear cells. J Neuroimmunol. 1996;66:115–23. - PubMed
-
- Navikas V, He B, Link J, et al. Augmented expression of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and lymphotoxin in mononuclear cells in multiple sclerosis and optic neuritis. Brain. 1996;119(Pt 1):213–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

