CD4+ CD25(high) Foxp3+ regulatory T cells downregulate human Vdelta2+ T-lymphocyte function triggered by anti-CD3 or phosphoantigen
- PMID: 19019089
- PMCID: PMC2712108
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02982.x
CD4+ CD25(high) Foxp3+ regulatory T cells downregulate human Vdelta2+ T-lymphocyte function triggered by anti-CD3 or phosphoantigen
Abstract
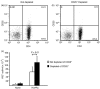
Vdelta2+ T cells, the major circulating T-cell receptor-gammadelta-positive (TCR-gammadelta+) T-cell subset in healthy adults, are involved in immunity against many microbial pathogens including Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Vdelta2+ T cells recognize small phosphorylated metabolites (phosphoantigens), expand in response to whole M. tuberculosis bacilli, and complement the protective functions of CD4+ T cells. CD4+ CD25(high) Foxp3+ T cells (Tregs) comprise 5-10% of circulating T cells and are increased in patients with active tuberculosis (TB). We investigated whether, in addition to their known role in suppressing TCR-alphabeta+ lymphocytes, Tregs suppress Vdelta2+ T-cell function. We found that depletion of Tregs from peripheral blood mononuclear cells increased Vdelta2+ T-cell expansion in response to M. tuberculosis (H37Ra) in tuberculin-skin-test-positive donors. We developed a suppression assay with fluorescence-activated cell sorting-purified Tregs and Vdelta2+ T cells by coincubating the two cell types at a 1 : 1 ratio. The Tregs partially suppressed interferon-gamma secretion by Vdelta2+ T cells in response to anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody plus interleukin-2 (IL-2). In addition, Tregs downregulated the Vdelta2+ T-cell interferon-gamma responses induced by phosphoantigen (BrHPP) and IL-2. Under the latter conditions there was no TCR stimulus for Tregs and therefore IL-2 probably triggered suppressor activity. Addition of purified protein derivative (PPD) increased the suppression of Vdelta2+ T cells, suggesting that PPD activated antigen-specific Tregs. Our study provides evidence that Tregs suppress both anti-CD3 and antigen-driven Vdelta2+ T-cell activation. Antigen-specific Tregs may therefore contribute to the Vdelta2+ T-cell functional deficiencies observed in TB.
Figures


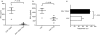

References
-
- Pedrazzini T, Hug K, Louis JA. Importance of L3T4+ and Lyt-2+ cells in the immunologic control of infection with Mycobacterium bovis strain bacillus Calmette–Guérin in mice. Assessment by elimination of T cell subsets in vivo. J Immunol. 1987;139:2032–7. - PubMed
-
- Orme IM, Collins FM. Adoptive protection of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected lung. Dissociation between cells that passively transfer protective immunity and those that transfer delayed-type hypersensitivity to tuberculin. Cell Immunol. 1984;84:113–20. - PubMed
-
- Ladel CH, Daugelat S, Kaufmann SH. Immune response to Mycobacterium bovis bacille Calmette–Guérin infection in major histocompatibility complex class I- and II-deficient knock-out mice: contribution of CD4 and CD8 T cells to acquired resistance. Eur J Immunol. 1995;25:377–84. - PubMed
-
- Flynn JL, Chan J. Immunology of tuberculosis. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:93–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

