Study protocol. A prospective cohort study of unselected primiparous women: the pregnancy outcome prediction study
- PMID: 19019223
- PMCID: PMC2611961
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2393-8-51
Study protocol. A prospective cohort study of unselected primiparous women: the pregnancy outcome prediction study
Abstract
Background: There have been dramatic changes in the approach to screening for aneuploidy over the last 20 years. However, the approach to screening for other complications of pregnancy such as intra-uterine growth restriction, pre-eclampsia and stillbirth remains largely unchanged. Randomised controlled trials of routine application of high tech screening methods to the general population have generally failed to show improvement in outcome. We have previously reviewed this and concluded it was due, in large part, to poor performance of screening tests. Here, we report a study design where the primary aim is to generate clinically useful methods to screen women to assess their risk of adverse pregnancy outcome.
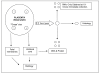
Methods/design: We report the design of a prospective cohort study of unselected primiparous women recruited at the time of their first ultrasound scan. Participation involves serial phlebotomy and obstetric ultrasound at the dating ultrasound scan (typically 10-14 weeks), 20 weeks, 28 weeks and 36 weeks gestation. In addition, maternal demographic details are obtained; maternal and paternal height are measured and maternal weight is serially measured during the pregnancy; maternal, paternal and offspring DNA are collected; and, samples of placenta and membranes are collected at birth. Data will be analysed as a prospective cohort study, a case-cohort study, and a nested case-control study.
Discussion: The study is expected to provide a resource for the identification of novel biomarkers for adverse pregnancy outcome and to evaluate the performance of biomarkers and serial ultrasonography in providing clinically useful prediction of risk.
Figures
References
-
- National Collaborating Centre for Women's and Children's Health . Antenatal care: routine care for the healthy pregnant woman. RCOG Press, London; 2008. - PubMed
-
- Gardosi J, Francis A. Controlled trial of fundal height measurement plotted on customised antenatal growth charts. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1999;106:309–317. - PubMed
-
- Information and Statistics Division NHS Scotland . Scottish perinatal and infant mortality report 2000. Edinburgh: ISD Scotland Publications; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical