The influence of high and low levels of estrogen on diurnal urine regulation in young women
- PMID: 19019246
- PMCID: PMC2626595
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2490-8-16
The influence of high and low levels of estrogen on diurnal urine regulation in young women
Abstract
Background: Sex hormones have a pronounced effect on arginine vasopressin (AVP), and therefore on the diurnal water homeostasis. Low and high levels of plasma-estradiol as seen in the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle may therefore alter the diurnal regulation of urine production. Furthermore the structural resemblance of oxytocin to vasopressin has led to speculations about the possible antidiuretic properties of oxytocin under normal physiological conditions. To elucidate the influence of high and low p-estradiol on the regulation of the diurnal urine production, 15 normal menstruating women (21-33 y) underwent two circadian in-patient investigations, both situated in follicular phase.
Methods: Admitting the participants solely in the follicular phase resulted in high and low plasma-estradiol whereas plasma-progesterone was similar. Urine and blood samples were taken at predetermined time points to determine plasma AVP, plasma oxytocin, plasma aldosterone, plasma natriuretic peptide (ANP), urinary solute excretions, and urinary excretions of prostaglandin E2 (PGE-2) and aquaporin-2 (AQP-2). Blood pressure was measured every hour.
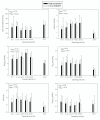
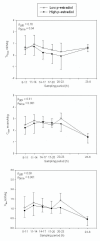
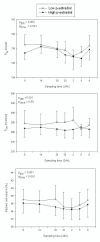
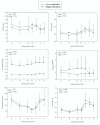
Results: Plasma AVP, plasma aldosterone and plasma ANP were unaffected by the different levels of estradiol. All had marked circadian variations whereas oxytocin did not display any circadian rhythm. High estradiol resulted in lower p-osmolality and p-sodium reflecting the downward resetting of the osmoreceptors. Oxytocin did not correlate with either diuresis or urine osmolality. The diurnal urine production was similar in the two groups as were urine osmolality, excretion of PGE-2 and AQP-2. AQP-2 does not have a circadian rhythm and is not significantly correlated to either AVP or oxytocin under normal physiological conditions.
Conclusion: High and low level of estradiol has no influence on the circadian rhythm of AVP or the subsequent urine production. High p-estradiol resets the osmoreceptors for AVP release. Furthermore it appears that oxytocin under normal physiological conditions do not contribute to the overall antidiuretic effect.
Figures
References
-
- Rittig S, Knudsen UB, Norgaard JP, Pedersen EB, Djurhuus JC. Abnormal diurnal rhythm of plasma vasopressin and urinary output in patients with enuresis. Am J Physiol. 1989;256:F664–F671. - PubMed
-
- Rittig S, Knudsen UB, Jonler M, Norgaard JP, Pedersen EB, Djurhuus JC. Adult enuresis. The role of vasopressin and atrial natriuretic peptide. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 1989;125:79–86. - PubMed
-
- George CP, Messerli FH, Genest J, Nowaczynski W, Boucher R, Kuchel Orofo-Oftega M. Diurnal variation of plasma vasopressin in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975;41:332–338. - PubMed
-
- Forsling ML, Montgomery H, Halpin D, Windle RJ, Treacher DF. Daily patterns of secretion of neurohypophysial hormones in man: effect of age. Exp Physiol. 1998;83:409–418. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

