Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2)/HIV-1 envelope chimeras detect high titers of broadly reactive HIV-1 V3-specific antibodies in human plasma
- PMID: 19019969
- PMCID: PMC2620909
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01743-08
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2)/HIV-1 envelope chimeras detect high titers of broadly reactive HIV-1 V3-specific antibodies in human plasma
Abstract
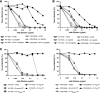
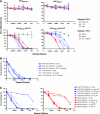
Deciphering antibody specificities that constrain human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope (Env) diversity, limit virus replication, and contribute to neutralization breadth and potency is an important goal of current HIV/AIDS vaccine research. Transplantation of discrete HIV-1 neutralizing epitopes into HIV-2 scaffolds may provide a sensitive, biologically functional context by which to quantify specific antibody reactivities even in complex sera. Here, we describe a novel HIV-2 proviral scaffold (pHIV-2(KR.X7)) into which we substituted the complete variable region 3 (V3) of the env gene of HIV-1(YU2) or HIV-1(Ccon) to yield the chimeric proviruses pHIV-2(KR.X7) YU2 V3 and pHIV-2(KR.X7) Ccon V3. These HIV-2/HIV-1 chimeras were replication competent and sensitive to selective pharmacological inhibitors of virus entry. V3 chimeric viruses were resistant to neutralization by HIV-1 monoclonal antibodies directed against the CD4 binding site, coreceptor binding site, and gp41 membrane proximal external region but exhibited striking sensitivity to HIV-1 V3-specific monoclonal antibodies, 447-52D and F425 B4e8 (50% inhibitory concentration of [IC(50)] <0.005 microg/ml for each). Plasma specimens from 11 HIV-1 clade B- and 10 HIV-1 clade C-infected subjects showed no neutralizing activity against HIV-2 but exhibited high-titer V3-specific neutralization against both HIV-2/HIV-1 V3 chimeras with IC(50) measurements ranging from 1:50 to greater than 1:40,000. Neutralization titers of B clade plasmas were as much as 1,000-fold lower when tested against the primary HIV-1(YU2) virus than with the HIV-2(KR.X7) YU2 V3 chimera, demonstrating highly effective shielding of V3 epitopes in the native Env trimer. This finding was replicated using a second primary HIV-1 strain (HIV-1(BORI)) and the corresponding HIV-2(KR.X7) BORI V3 chimera. We conclude that V3 is highly immunogenic in vivo, eliciting antibodies with substantial breadth of reactivity and neutralizing potential. These antibodies constrain HIV-1 Env to a structure(s) in which V3 epitopes are concealed prior to CD4 engagement but do not otherwise contribute to neutralization breadth and potency against most primary virus strains. Triggering of the viral spike to reveal V3 epitopes may be required if V3 immunogens are to be components of an effective HIV-1 vaccine.
Figures

References
-
- Albert, J., B. Abrahamsson, K. Nagy, E. Aurelius, H. Gaines, G. Nystrom, and E. M. Fenyo. 1990. Rapid development of isolate-specific neutralizing antibodies after primary HIV-1 infection and consequent emergence of virus variants which resist neutralization by autologous sera. AIDS 4107-112. - PubMed
-
- Beutler, E., M. A. Lichtman, B. S. Coller, T. J. Kipps, and U. Seligsohn. 2000. Williams hematology, 6th ed. McGraw-Hill Professional, New York, NY.
-
- Binley, J. M., E. A. Lybarger, E. T. Crooks, M. S. Seaman, E. Gray, K. L. Davis, J. M. Decker, D. Wycuff, L. Harris, N. Hawkins, B. Wood, C. Nathe, D. Richman, G. D. Tomaras, F. Bibollet-Ruche, J. E. Robinson, L. Morris, G. M. Shaw, D. C. Montefiori, and J. R. Mascola. 2008. Profiling the specificity of neutralizing antibodies in a large panel of plasmas from patients chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtypes B and C. J. Virol. 8211651-11668. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Binley, J. M., T. Wrin, B. Korber, M. B. Zwick, M. Wang, C. Chappey, G. Stiegler, R. Kunert, S. Zolla-Pazner, H. Katinger, C. J. Petropoulos, and D. R. Burton. 2004. Comprehensive cross-clade neutralization analysis of a panel of anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 7813232-13252. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

