Role of nitric oxide signaling components in differentiation of embryonic stem cells into myocardial cells
- PMID: 19020077
- PMCID: PMC2596213
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0810230105
Role of nitric oxide signaling components in differentiation of embryonic stem cells into myocardial cells
Abstract
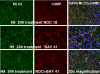
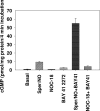
Nitric oxide (NO) is involved in number of physiological and pathological events. Our previous studies demonstrated a differential expression of NO signaling components in mouse and human ES cells. Here, we demonstrate the effect of NO donors and soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) activators in differentiation of ES cells into myocardial cells. Our results with mouse and human ES cells demonstrate an increase in Nkx2.5 and myosin light chain (MLC2) mRNA expression on exposure of cells to NO donors and a decrease in mRNA expression of both cardiac-specific genes with nonspecific NOS inhibitor and a concomitant increase and decrease in the mRNA levels of sGC alpha(1) subunit. Although sGC activators alone exhibited an increase in mRNA expression of cardiac genes (MLC2 and Nkx2.5), robust inductions of mRNA and protein expression of marker genes were observed when NO donors and sGC activators were combined. Measurement of NO metabolites revealed an increase in the nitrite levels in the conditioned media and cell lysates on exposure of cells to the different concentrations of NO donors. cGMP analysis in undifferentiated stem cells revealed a lack of stimulation with NO donors. Differentiated cells however, acquired the ability to be stimulated by NO donors. Although, 3-(4-amino-5-cyclopropylpyrimidin-2-yl)-1-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1H-pyrazolo [3,4-b]pyridine (BAY 41-2272) alone was able to stimulate cGMP accumulation, the combination of NO donors and BAY 41-2272 stimulated cGMP levels more than either of the agents separately. These studies demonstrate that cGMP-mediated NO signaling plays an important role in the differentiation of ES cells into myocardial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
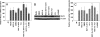
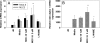

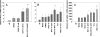
References
-
- Thomson JA, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1997;282:1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Reubinoff BE, Pera MF, Fong CY, Trounson A, Bongso A. Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: Somatic differentiation in vitro. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18:399–404. - PubMed
-
- Hescheler J, et al. Embryonic stem cells: A model to study structural and functional properties in cardiomyogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. 1997;36:149–162. - PubMed
-
- Min JY, et al. Transplantation of embryonic stem cells improves cardiac function in postinfarcted rats. J Appl Physiol. 2002;92:288–296. - PubMed
-
- Min JY, et al. Long-term improvement of cardiac function in rats after infarction by transplantation of embryonic stem cells. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;125:361–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

