Building epithelial tissues from skin stem cells
- PMID: 19022769
- PMCID: PMC2693088
- DOI: 10.1101/sqb.2008.73.032
Building epithelial tissues from skin stem cells
Abstract
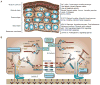
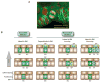
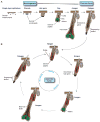
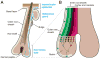
The skin epidermis and its appendages provide a protective barrier that guards against loss of fluids, physical trauma, and invasion by harmful microbes. To perform these functions while confronting the harsh environs of the outside world, our body surface undergoes constant rejuvenation through homeostasis. In addition, it must be primed to repair wounds in response to injury. The adult skin maintains epidermal homeostasis, hair regeneration, and wound repair through the use of its stem cells. What are the properties of skin stem cells, when do they become established during embryogenesis, and how are they able to build tissues with such remarkably distinct architectures? How do stem cells maintain tissue homeostasis and repair wounds and how do they regulate the delicate balance between proliferation and differentiation? What is the relationship between skin cancer and mutations that perturbs the regulation of stem cells? In the past 5 years, the field of skin stem cells has bloomed as we and others have been able to purify and dissect the molecular properties of these tiny reservoirs of goliath potential. We report here progress on these fronts, with emphasis on our laboratory's contributions to the fascinating world of skin stem cells.
Figures

References
-
- Alonso L, Fuchs E. The hair cycle. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:391–393. - PubMed
-
- Andl T, Reddy ST, Gaddapara T, Millar SE. WNT signals are required for the initiation of hair follicle development. Dev Cell. 2002;2:643–653. - PubMed
-
- Andl T, Ahn K, Kairo A, Chu EY, Wine-Lee L, Reddy ST, Croft NJ, Cebra-Thomas JA, Metzger D, Chambon P, et al. Epithelial Bmpr1a regulates differentiation and proliferation in postnatal hair follicles and is essential for tooth development. Development. 2004;131:2257–2268. - PubMed
-
- Arnold I, Watt FM. c-Myc activation in transgenic mouse epidermis results in mobilization of stem cells and differentiation of their progeny. Curr Biol. 2001;11:558–568. - PubMed
-
- Balzac F, Avolio M, Degani S, Kaverina I, Torti M, Silengo L, Small JV, Retta SF. E-cadherin endocytosis regulates the activity of Rap1: A traffic light GTPase at the crossroads between cadherin and integrin function. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:4765–4783. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
