Prolactin activates mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and corticotropin releasing hormone transcription in rat hypothalamic neurons
- PMID: 19022892
- PMCID: PMC2659278
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2008-1023
Prolactin activates mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling and corticotropin releasing hormone transcription in rat hypothalamic neurons
Abstract
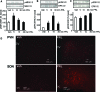
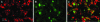
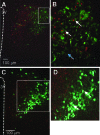
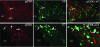
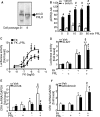
Prolactin (PRL) modulates maternal behavior and mediates hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis inhibition during lactation via PRL receptors in the brain. To identify mechanisms mediating these effects, we examined the effects of PRL on signaling and CRH transcription in hypothalamic neurons in vivo and in vitro. Western blot of hypothalamic proteins from rats receiving intracerebroventricular PRL injection revealed increases in phosphorylation of the MAPK and ERK. Double-staining immunohistochemistry demonstrated phosphorylated ERK localization in parvocellular CRH neurons as well as magnocellular vasopressin and oxytocin neurons of the hypothalamic paraventricular (PVN) and supraoptic nuclei. PRL also induced ERK phosphorylation in vitro in the hypothalamic cell line, 4B, which expresses PRL receptors, and in primary hypothalamic neuronal cultures. Using reporter gene assays in 4B cells, or quantitative RT-PCR for primary transcript in hypothalamic cell cultures, PRL potentiated forskolin-stimulated CRH transcription through activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway. The effect of PRL in hypothalamic cell cultures was unaffected by tetrodotoxin, suggesting a direct effect on CRH neurons. The data show that PRL activates the ERK/MAPK pathway and facilitates CRH transcription in CRH neurons, suggesting that the inhibitory effect of PRL on hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis activity reported in vivo is indirect and probably mediated through modulation of afferent pathways to the PVN. In addition, the prominent stimulatory action of PRL on the ERK/MAPK pathway in the hypothalamic PVN and supraoptic nucleus is likely to mediate neuroplasticity of the neuroendocrine system during lactation.
Figures
References
-
- Mangurian LP, Walsh RJ, Posner BI 1992 Prolactin enhancement of its own uptake at the choroid plexus. Endocrinology 131:698–702 - PubMed
-
- Walsh R, Slaby F, Posner B 1987 A receptor-mediated mechanism for the transport of prolactin from blood to cerebrospinal fluid. Endocrinology 120:1846–1850 - PubMed
-
- Ben-Jonathan N, Mershon JL, Allen DL, Steinmetz RW 1996 Extrapituitary prolactin: distribution, regulation, functions, and clinical aspects. Endocr Rev 17:639–669 - PubMed
-
- Clapp C, Torner L, Gutierrez-Ospina G, Alcantara E, Lopez-Gomez F, Nagano M, Kellly P, Mejia S, Ma M, Martinez de la Escalera G 1994 The prolactin gene is expressed in the hypothalamic-neurohypophyseal system and the protein is processed into a 14-kDa fragment with activity like 16-kDa prolactin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:10384–10388 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Emanuele N, Jurgens J, Halloran M, Tentler J, Lawrence A, Kelley M 1992 The rat prolactin gene is expressed in brain tissue: detection of normal and alternatively spliced prolactin messenger RNA. Mol Endocrinol 6:35–42 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

