Intermolecular interactions identify ligand-selective activity of estrogen receptor alpha/beta dimers
- PMID: 19022902
- PMCID: PMC2596243
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0807274105
Intermolecular interactions identify ligand-selective activity of estrogen receptor alpha/beta dimers
Abstract
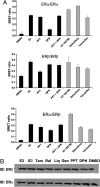
Estrogen receptor (ER) dimerization is prerequisite for its activation of target gene transcription. Because the two forms of ER, ERalpha and ERbeta, exhibit opposing functions in cell proliferation, the ability of ligands to induce ERalpha/beta heterodimers vs. their respective homodimers is expected to have profound impacts on transcriptional outcomes and cellular growth. However, there is a lack of direct methods to monitor the formation of ERalpha/beta heterodimers in vivo and to distinguish the ability of estrogenic ligands to promote ER homo- vs. heterodimerization. Here, we describe bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) assays for monitoring the formation of ERalpha/beta heterodimers and their respective homodimers in live cells. We demonstrate that although both partners contribute to heterodimerization, ligand-bound ERalpha plays a dominant role. Furthermore, a bioactive component was found to induce ERbeta/beta homodimers, and ERalpha/beta heterodimers but had minimal activity on ERalpha/alpha homodimers, posing a model that compounds promoting ERalpha/beta heterodimer formation might have therapeutic value. Thus, ER homodimer and heterodimer BRET assays are applicable to drug screening for dimer-selective selective ER modulators. Furthermore, this strategy can be used to study other nuclear receptor dimers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
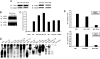
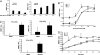


Similar articles
-
A Computational-Based Approach to Identify Estrogen Receptor α/β Heterodimer Selective Ligands.Mol Pharmacol. 2018 Mar;93(3):197-207. doi: 10.1124/mol.117.108696. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Mol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29295894 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo molecular imaging of estrogen receptor α and β homo- and heterodimerization: exploration of new modes of receptor regulation.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Dec;25(12):2029-40. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1145. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 22052998 Free PMC article.
-
Differential requirements of Hsp90 and DNA for the formation of estrogen receptor homodimers and heterodimers.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 21;285(21):16125-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.104356. Epub 2010 Mar 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20353944 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor beta: an overview and update.Nucl Recept Signal. 2008 Feb 1;6:e003. doi: 10.1621/nrs.06003. Nucl Recept Signal. 2008. PMID: 18301783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen receptor α and β in the normal immune system and in lymphoid malignancies.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Aug 15;375(1-2):121-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.05.016. Epub 2013 May 23. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23707618 Review.
Cited by
-
HMGB1 promotes the development of castration‑resistant prostate cancer by regulating androgen receptor activation.Oncol Rep. 2022 Nov;48(5):197. doi: 10.3892/or.2022.8412. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36129149 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen directly and specifically downregulates NaPi-IIa through the activation of both estrogen receptor isoforms (ERα and ERβ) in rat kidney proximal tubule.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 Mar 15;308(6):F522-34. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00386.2014. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25608964 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing the estrogen receptor modulator raloxifene to treat SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cell Death Differ. 2022 Jan;29(1):156-166. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00844-6. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Cell Death Differ. 2022. PMID: 34404919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Estrogen in Mitochondrial Disease.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul 11;45(1):68. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01592-8. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40643846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of estrogen receptor dimer selective ligands reveals growth-inhibitory effects on cells that co-express ERα and ERβ.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030993. Epub 2012 Feb 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22347418 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Helguero LA, Faulds MH, Gustafsson JA, Haldosen LA. Estrogen receptors α (ERα) and β (ERβ) differentially regulate proliferation and apoptosis of the normal murine mammary epithelial cell line HC11. Oncogene. 2005;24:6605–6616. - PubMed
-
- Dotzlaw H, Leygue E, Watson PH, Murphy LC. Expression of estrogen receptor-β in human breast tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82:2371–2374. - PubMed
-
- Omoto Y, et al. Clinical value of the wild-type estrogen receptor β expression in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2001;163:207–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

