Hyperbaric oxygen stimulates vasculogenic stem cell growth and differentiation in vivo
- PMID: 19023021
- PMCID: PMC2644249
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.91054.2008
Hyperbaric oxygen stimulates vasculogenic stem cell growth and differentiation in vivo
Abstract
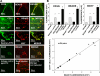
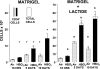
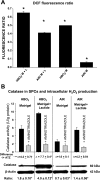
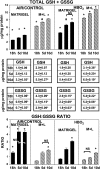
We hypothesized that oxidative stress from hyperbaric oxygen (HBO(2), 2.8 ATA for 90 min daily) exerts a trophic effect on vasculogenic stem cells. In a mouse model, circulating stem/progenitor cell (SPC) recruitment and differentiation in subcutaneous Matrigel were stimulated by HBO(2) and by a physiological oxidative stressor, lactate. In combination, HBO(2) and lactate had additive effects. Vascular channels lined by CD34(+) SPCs were identified. HBO(2) and lactate accelerated channel development, cell differentiation based on surface marker expression, and cell cycle entry. CD34(+) SPCs exhibited increases in thioredoxin-1 (Trx1), Trx reductase, hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF)-1, -2, and -3, phosphorylated mitogen-activated protein kinases, vascular endothelial growth factor, and stromal cell-derived factor-1. Cell recruitment to Matrigel and protein synthesis responses were abrogated by N-acetyl cysteine, dithioerythritol, oxamate, apocynin, U-0126, neutralizing anti-vascular endothelial growth factor, or anti-stromal cell-derived factor-1 antibodies, and small inhibitory RNA to Trx reductase, lactate dehydrogenase, gp91(phox), HIF-1 or -2, and in mice conditionally null for HIF-1 in myeloid cells. By causing an oxidative stress, HBO(2) activates a physiological redox-active autocrine loop in SPCs that stimulates vasculogenesis. Thioredoxin system activation leads to elevations in HIF-1 and -2, followed by synthesis of HIF-dependent growth factors. HIF-3 has a negative impact on SPCs.
Figures


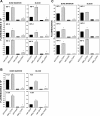
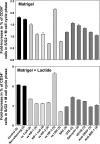

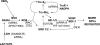
References
-
- Adams JD, Lauterburg BH, Mitchell JR. Plasma glutathione and glutathione disulfide in the rat: regulation and response to oxidative stress. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227: 749–754, 1983. - PubMed
-
- Ali M, Yasui F, Matsugo S, Konishi T. The lactate-dependent enhancement of hydroxyl radical generation by the Fenton reaction. Free Radic Res 32: 429–438, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Andoh T, Chiueh C, Chock P. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase regulates the expression of thioredoxin and thioredoxin peroxidase-1 during hormesis in response to oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 278: 885–890, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Arai R, Masutani H, Yodoi J, Debbas V, Laurindo F, Stern A, Monteiro H. Nitric oxide induces thioredoxin-1 nuclear translocation: possible association with the p21Ras survival pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348: 1254–1260, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, Silver M, van der Zee R, Li T, Witzenbichler B, Schatteman G, Isner JM. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science 275: 964–967, 1997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

