Patient centeredness, cultural competence and healthcare quality
- PMID: 19024223
- PMCID: PMC2824588
- DOI: 10.1016/s0027-9684(15)31505-4
Patient centeredness, cultural competence and healthcare quality
Abstract
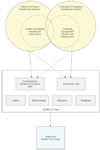
Cultural competence and patient centeredness are approaches to improving healthcare quality that have been promoted extensively in recent years. In this paper, we explore the historical evolution of both cultural competence and patient centeredness. In doing so, we demonstrate that early conceptual models of cultural competence and patient centeredness focused on how healthcare providers and patients might interact at the interpersonal level and that later conceptual models were expanded to consider how patients might be treated by the healthcare system as a whole. We then compare conceptual models for both cultural competence and patient centeredness at both the interpersonal and healthcare system levels to demonstrate similarities and differences. We conclude that, although the concepts have had different histories and foci, many of the core features of cultural competence and patient centeredness are the same. Each approach holds promise for improving the quality of healthcare for individual patients, communities and populations.
Figures




References
-
- Lipkin M, Jr, Quill TE, Napodano RJ. The medical interview: a core curriculum for residencies in internal medicine. Ann Intern Med. 1984;100:277–284. - PubMed
-
- Levenstein JH, McCracken EC, McWhinney IR, et al. The patient-centred clinical method. 1. A model for the doctor-patient interaction in family medicine. Fam Pract. 1986;3:24–30. - PubMed
-
- Stewart M, Brown J, Weston W, et al. Patient-Centered Medicine: Transforming the Clinical Method. London: Sage; 1995.
-
- Mead N, Bower P. Patient-centeredness: a conceptual framework and review of the empirical literature. Soc Sci Med. 2000;51:1087–1110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

