Tolerance induced via TLR2 and TLR4 in human dendritic cells: role of IRAK-1
- PMID: 19025640
- PMCID: PMC2628880
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-9-69
Tolerance induced via TLR2 and TLR4 in human dendritic cells: role of IRAK-1
Abstract
Background: While dendritic cells (DCs) can induce tolerance in T cells, little is known about tolerance induction in DCs themselves. We have analysed tolerance induced in human in-vitro generated DCs by repeated stimulation with ligands for TLR4 and TLR2.
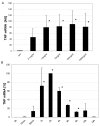
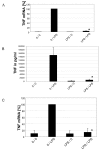
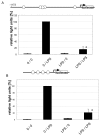
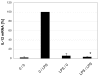
Results: DCs stimulated with the TLR4 ligand LPS did show a rapid and pronounced expression of TNF mRNA and protein. When DCs were pre-cultured for 2 days with 5 ng LPS/ml then the subsequent response to stimulation with a high dose of LPS (500 ng/ml) was strongly reduced for both TNF mRNA and protein. At the promoter level there was a reduced transactivation by the -1173 bp TNF promoter and by a construct with a tetrameric NF-kappaB motif. Within the signalling cascade leading to NF-kappaB activation we found an ablation of the IRAK-1 adaptor protein in LPS-tolerant DCs. Pre-culture of DCs with the TLR2 ligand Pam3Cys also led to tolerance with respect to TNF gene expression and IRAK-1 protein was ablated in such tolerant cells as well, while IRAK-4 protein levels were unchanged.
Conclusion: These data show that TLR-ligands can render DCs tolerant with respect to TNF gene expression by a mechanism that likely involves blockade of signal transduction at the level of IRAK-1.
Figures
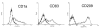


References
-
- Ziegler-Heitbrock HW, Wedel A, Schraut W, Strobel M, Wendelgass P, Sternsdorf T, Bauerle PA, Haas JG, Riethmuller G. Tolerance to lipopolysaccharide involves mobilization of nuclear factor kappa B with predominance of p50 homodimers. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:17001–4. - PubMed
-
- Adib-Conquy M, Cavaillon JM. Gamma interferon and granulocyte/monocyte colony-stimulating factor prevent endotoxin tolerance in human monocytes by promoting interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase expression and its association to MyD88 and not by modulating TLR4 expression. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:27927–34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200705200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Siedlar M, Frankenberger M, Benkhart E, Espevik T, Quirling M, Brand K, Zembala M, Ziegler-Heitbrock L. Tolerance induced by the lipopeptide Pam3Cys is due to ablation of IL-1R-associated kinase-1. J Immunol. 2004;173:2736–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

