Enhancement of the endosomal endocytic pathway increases quantal size
- PMID: 19026748
- PMCID: PMC4522282
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2008.10.005
Enhancement of the endosomal endocytic pathway increases quantal size
Abstract
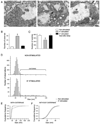
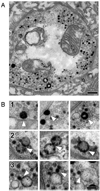
We combined recordings of spontaneous quantal events with electron microscopy analysis of synaptic ultrastructure to demonstrate that the size of a neurosecretory quantum increases following an activation of the endosomal endocytic pathway. We reversibly activated the endosomal endocytic pathway in Drosophila motor boutons by application of high K+ solution. This treatment produced the formation of numerous cisternae, vacuoles and enlarged vesicles. Spontaneous quantal events recorded immediately after the cessation of high K+ application were significantly enlarged, and this increase in quantal size was reversed after a 10 minute resting period. Actin depolymerization produced by latrunculin B pretreatment inhibited both the formation of endosome-like structures and the increase in quantal size. Loading the preparations with the dye FM1-43 followed by photoconversion of the dye combined with electron microscopy analysis revealed that the observed cisternae are likely to be the product of both bulk membrane retrieval and vesicle fusion.
Figures





References
-
- Atwood HL, Govind CK, Wu CF. Differential ultrastructure of synaptic terminals on ventral longitudinal abdominalmuscles in Drosophila larvae. J. Neurobiol. 1993;24:1008–1024. - PubMed
-
- Bekkers JM, Stevens CF. Quantal analysis of EPSCs recorded from small numbers of synapses in hippocampal cultures. J. Neurophysiol. 1995;73:1145–1156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

