The 14-3-3 proteins: integrators of diverse signaling cues that impact cell fate and cancer development
- PMID: 19027299
- PMCID: PMC3073487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.10.003
The 14-3-3 proteins: integrators of diverse signaling cues that impact cell fate and cancer development
Abstract
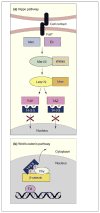
The highly conserved 14-3-3 protein family has risen to a position of importance in cell biology owing to its involvement in vital cellular processes, such as metabolism, protein trafficking, signal transduction, apoptosis and cell-cycle regulation. The 14-3-3 proteins are phospho-serine/phospho-threonine binding proteins that interact with a diverse array of binding partners. Because many 14-3-3 interactions are phosphorylation-dependent, 14-3-3 has been tightly integrated into the core phospho-regulatory pathways that are crucial for normal growth and development and that often become dysregulated in human disease states such as cancer. This review examines the recent advances that further elucidate the role of 14-3-3 proteins as integrators of diverse signaling cues that influence cell fate decisions and tumorigenesis.
Figures



References
-
- Aitken A. 14-3-3 proteins: a historic overview. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16:162–172. - PubMed
-
- Moore BW, Perez VJ. Specific Acid Proteins in the Nervous System. Prentice-Hall; 1967.
-
- Gardino AK, et al. Structural determinants of 14-3-3 binding specificities and regulation of subcellular localization of 14-3-3-ligand complexes: a comparison of the X-ray crystal structures of all human 14-3-3 isoforms. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16:173–182. - PubMed
-
- Tzivion G, et al. 14-3-3 proteins as potential oncogenes. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006;16:203–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

