From nature to the laboratory and into the clinic
- PMID: 19028103
- PMCID: PMC2665039
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.10.089
From nature to the laboratory and into the clinic
Abstract
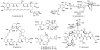
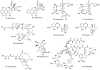
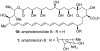
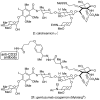
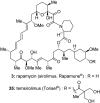
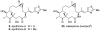
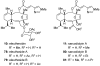
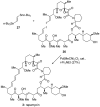
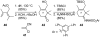
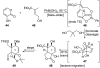
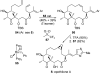
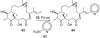
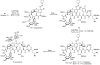
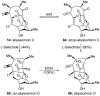
Natural products possess a broad diversity of structure and function, and they provide inspiration for chemistry, biology, and medicine. In this review article, we highlight and place in context our laboratory's total syntheses of, and related studies on, complex secondary metabolites that were clinically important drugs, or have since been developed into useful medicines, namely amphotericin B (1), calicheamicin gamma(1)(I) (2), rapamycin (3), Taxol (4), the epothilones [e.g., epothilones A (5) and B (6)], and vancomycin (7). We also briefly highlight our research with other selected inspirational natural products possessing interesting biological activities [i.e., dynemicin A (8), uncialamycin (9), eleutherobin (10), sarcodictyin A (11), azaspiracid-1 (12), thiostrepton (13), abyssomicin C (14), platensimycin (15), platencin (16), and palmerolide A (17)].
Figures










References
-
- Nicolaou KC, Montagnon T. Molecules That Changed the World. Wiley-VCH; Weinheim: 2008. p. 366.
-
- Nicolaou KC, Guy RK, Gunzner JL. Medchem News. 1997;3:12.
-
-
Isolation:Vandeputte J, Watchtel JL, Stiller ET. Antibiot. Annu. 1956:587.structure determination:Mechinski W, Shaffner CP, Ganis P, Avitabile G. Tetrahedron Lett. 1970;11:3873.Ganis P, Avitabile G, Mechinski W, Shaffner CP. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1971;93:4560.
-
-
- Omura S, editor. Macrolide Antibiotics, Chemistry, Biology and Practice. Academic; New York: 1984. p. 635.
- Tereshin IM. Polyene Antibiotics-Present and Future. University of Tokyo; Tokyo: 1976. p. 160.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

