Modeling the dynamics of transcriptional gene regulatory networks for animal development
- PMID: 19028486
- PMCID: PMC4100934
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.10.043
Modeling the dynamics of transcriptional gene regulatory networks for animal development
Abstract
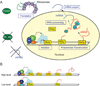
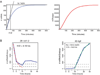
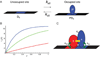
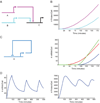
The dynamic process of cell fate specification is regulated by networks of regulatory genes. The architecture of the network defines the temporal order of specification events. To understand the dynamic control of the developmental process, the kinetics of mRNA and protein synthesis and the response of the cis-regulatory modules to transcription factor concentration must be considered. Here we review mathematical models for mRNA and protein synthesis kinetics which are based on experimental measurements of the rates of the relevant processes. The model comprises the response functions of cis-regulatory modules to their transcription factor inputs, by incorporating binding site occupancy and its dependence on biologically measurable quantities. We use this model to simulate gene expression, to distinguish between cis-regulatory execution of "AND" and "OR" logic functions, rationalize the oscillatory behavior of certain transcriptional auto-repressors and to show how linked subcircuits can be dealt with. Model simulations display the effects of mutation of binding sites, or perturbation of upstream gene expression. The model is a generally useful tool for understanding gene regulation and the dynamics of cell fate specification.
Figures

References
-
- Amore G, Davidson EH. cis-Regulatory control of cyclophilin, a member of the ETS-DRI skeletogenic gene battery in the sea urchin embryo. Dev. Biol. 2006;293:555–564. - PubMed
-
- Arnosti DN, Barolo S, Levine M, Small S. The eve stripe 2 enhancer employs multiple modes of transcriptional synergy. Development. 1996;122:205–214. - PubMed
-
- Aronson AI, Chen K. Rates of RNA chain growth in developing sea urchin embryos. Dev. Biol. 1977;59:39–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

