Impaired NHEJ function in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 19028508
- PMCID: PMC2875794
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.10.019
Impaired NHEJ function in multiple myeloma
Abstract
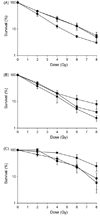
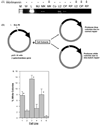
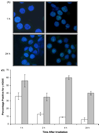
Multiple myeloma (MM) is characterized by multiple chromosomal aberrations. To assess the contribution of DNA repair to this phenotype, ionizing radiation was used to induce DNA double strand breaks in three MM cell lines. Clonogenic survival assays showed U266 (SF4=15.3+6.4%) and RPMI 8226 (SF4=12.6.0+1.7%) were radiation sensitive while OPM2 was resistant (SF4=78.9+4.1%). Addition of the DNA-PK inhibitor NU7026 showed the expected suppression in radiation survival in OPM2 but increased survival in both radiation sensitive cell lines. To examine non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) repair in these lines, the ability of protein extracts to support in vitro DNA repair was measured. Among the three MM cell lines analyzed, RPMI 8226 demonstrated impaired blunt ended DNA ligation using a ligation-mediated PCR technique. In a bacterial based functional assay to rejoin a DNA break within the beta-galactosidase gene, RPMI 8226 demonstrated a 4-fold reduction in rejoining fidelity compared to U266, with OPM2 showing an intermediate capacity. Ionizing radiation induced a robust gamma-H2AX response in OPM2 but only a modest increase in each radiation sensitive cell line perhaps related to the high level of gamma-H2AX in freshly plated cells. Examination of gamma-H2AX foci in RPMI 8226 cells confirmed data from Western blots where a significant number of foci were present in freshly plated untreated cells which diminished over 24h of culture. Based on the clonogenic survival and functional repair assays, all three cell lines exhibited corrupt NHEJ repair. We conclude that suppression of aberrant NHEJ function using the DNA-PK inhibitor NU7026 may facilitate access of DNA ends to an intact homologous recombination repair pathway, paradoxically increasing survival after irradiation. These data provide insight into the deregulation of DNA repair at the site of DNA breaks in MM that may underpin the characteristic genomic instability of this disease.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Calasanz MJ, Cigudosa JC, Odero MD, Ferreira C, Ardanaz MT, Fraile A, Carrasco JL, Sole F, Cuesta B, Gullon A. Cytogenetic analysis of 280 patients with multiple myeloma and related disorders: primary breakpoints and clinical correlations. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1997;18:84–93. - PubMed
-
- Rajkumar S, Fonseca R, Lacy M, Witzig T, Lust J, Greipp P, Therneau T, Kyle R, Litzow M, Gertz M. Abnormal cytogenetics predict poor survival after high-dose therapy and autologous blood cell transplantation in multiple myeloma. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999;24:497–503. - PubMed
-
- San Miguel JF, Garcia-Sanz R, Gonzalez M, Orfao A. DNA cell content studies in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Lymphoma. 1996;23:33–41. - PubMed
-
- Smadja NV, Bastard C, Brigaudeau C, Leroux D, Fruchart C. Hypodiploidy is a major prognostic factor in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2001;98:2229–2238. - PubMed
-
- Bergsagel PL, Kuehl WM. Chromosome translocations in multiple myeloma. Oncogene. 2001;20:5611–5622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

