Conformation of the signal recognition particle in ribosomal targeting complexes
- PMID: 19029307
- PMCID: PMC2612770
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.1285609
Conformation of the signal recognition particle in ribosomal targeting complexes
Abstract
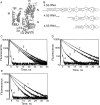
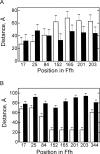
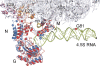
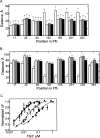
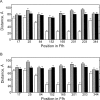
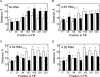
The bacterial signal recognition particle (SRP) binds to ribosomes synthesizing inner membrane proteins and, by interaction with the SRP receptor, FtsY, targets them to the translocon at the membrane. Here we probe the conformation of SRP and SRP protein, Ffh, at different stages of targeting by measuring fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between fluorophores placed at various positions within SRP. Distances derived from FRET indicate that SRP binding to nontranslating ribosomes triggers a global conformational change of SRP that facilitates binding of the SRP receptor, FtsY. Binding of SRP to a signal-anchor sequence exposed on a ribosome-nascent chain complex (RNC) causes a further change of the SRP conformation, involving the flexible part of the Ffh(M) domain, which increases the affinity for FtsY of ribosome-bound SRP up to the affinity exhibited by the isolated NG domain of Ffh. This indicates that in the RNC-SRP complex the Ffh(NG) domain is fully exposed for binding FtsY to form the targeting complex. Binding of FtsY to the RNC-SRP complex results in a limited conformational change of SRP, which may initiate subsequent targeting steps.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Domain rearrangement of SRP protein Ffh upon binding 4.5S RNA and the SRP receptor FtsY.RNA. 2005 Jun;11(6):947-57. doi: 10.1261/rna.7242305. RNA. 2005. PMID: 15923378 Free PMC article.
-
The bacterial SRP receptor, SecA and the ribosome use overlapping binding sites on the SecY translocon.Traffic. 2011 May;12(5):563-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01167.x. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Traffic. 2011. PMID: 21255212
-
The signal recognition particle binds to protein L23 at the peptide exit of the Escherichia coli ribosome.RNA. 2003 May;9(5):566-73. doi: 10.1261/rna.2196403. RNA. 2003. PMID: 12702815 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, function and evolution of the signal recognition particle.EMBO J. 2003 Jul 15;22(14):3479-85. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg337. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12853463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics of co-translational protein targeting.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2015 Dec;29:79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2015.09.016. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 26517565 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Domain Organization in the 54-kDa Subunit of the Chloroplast Signal Recognition Particle.Biophys J. 2016 Sep 20;111(6):1151-1162. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.08.004. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27653474 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of MAPK pathway ERK1/2 or p38 prevent the IL-1{beta}-induced up-regulation of SRP72 autoantigen in Jurkat cells.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 22;285(43):32824-32833. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.121087. Epub 2010 Aug 19. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20729213 Free PMC article.
-
The ribosome as a platform for co-translational processing, folding and targeting of newly synthesized proteins.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Jun;16(6):589-97. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1614. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19491936 Review.
-
Signal sequence-independent SRP-SR complex formation at the membrane suggests an alternative targeting pathway within the SRP cycle.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Jul 1;22(13):2309-23. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-02-0152. Epub 2011 May 5. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21551068 Free PMC article.
-
Predominant membrane localization is an essential feature of the bacterial signal recognition particle receptor.BMC Biol. 2009 Nov 13;7:76. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-7-76. BMC Biol. 2009. PMID: 19912622 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batey R.T., Rambo R.P., Lucast L., Rha B., Doudna J.A. Crystal structure of the ribonucleoprotein core of the signal recognition particle. Science. 2000;287:1232–1239. - PubMed
-
- Batey R.T., Sagar M.B., Doudna J.A. Structural and energetic analysis of RNA recognition by a universally conserved protein from the signal recognition particle. J. Mol. Biol. 2001;307:229–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
