Molecular architecture of inner dynein arms in situ in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii flagella
- PMID: 19029338
- PMCID: PMC2592835
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200808050
Molecular architecture of inner dynein arms in situ in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii flagella
Abstract
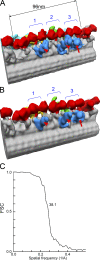
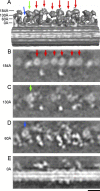
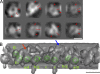
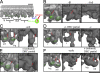
The inner dynein arm regulates axonemal bending motion in eukaryotes. We used cryo-electron tomography to reconstruct the three-dimensional structure of inner dynein arms from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. All the eight different heavy chains were identified in one 96-nm periodic repeat, as expected from previous biochemical studies. Based on mutants, we identified the positions of the AAA rings and the N-terminal tails of all the eight heavy chains. The dynein f dimer is located close to the surface of the A-microtubule, whereas the other six heavy chain rings are roughly colinear at a larger distance to form three dyads. Each dyad consists of two heavy chains and has a corresponding radial spoke or a similar feature. In each of the six heavy chains (dynein a, b, c, d, e, and g), the N-terminal tail extends from the distal side of the ring. To interact with the B-microtubule through stalks, the inner-arm dyneins must have either different handedness or, more probably, the opposite orientation of the AAA rings compared with the outer-arm dyneins.
Figures


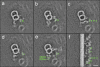

References
-
- Bozkurt, H.H., and D.M. Woolley. 1993. Morphology of nexin links in relation to interdoublet sliding in the sperm flagellum. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton. 24:109–118. - PubMed
-
- Burgess, S.A., D.A. Carter, S.D. Dover, and D.M. Woolley. 1991. The inner dynein arm complex: compatible images from freeze-etch and thin section methods of microscopy. J. Cell Sci. 100:319–328. - PubMed
-
- Burgess, S.A., M.L. Walker, H. Sakakibara, P.J. Knight, and K. Oiwa. 2003. Dynein structure and power stroke. Nature. 421:715–718. - PubMed
-
- Burgess, S.A., M.L. Walker, H. Sakakibara, H. Oiwa, and P.J. Knight. 2004. The structure of dynein-c by negative stain electron microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 146:205–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

