Determinants of the distribution and severity of hypoperfusion in patients with ischemic stroke
- PMID: 19029520
- PMCID: PMC2676970
- DOI: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000335929.06390.d3
Determinants of the distribution and severity of hypoperfusion in patients with ischemic stroke
Abstract
Background: In acute cerebral ischemia, two variables characterize the extent of hypoperfusion: the volume of hypoperfused tissue and the intensity of hypoperfusion within these regions. We evaluated the determinants of the intensity of hypoperfusion within oligemic regions among patients who were eligible for recanalization therapy for acute ischemic stroke.
Methods: We analyzed data, including pretreatment diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and perfusion-weighted imaging, on 119 patients with acute middle cerebral artery infarctions. The intensity of hypoperfusion within oligemic regions was characterized by the hypoperfusion intensity ratio (HIR), defined as the volume of tissue with severe hypoperfusion (Tmax > or = 8 seconds) divided by the volume of tissue with any hypoperfusion (Tmax > or = 2 seconds). Based on the DWI data, we divided the patients into four stroke phenotypes: large cortical, small (< 1 cm diameter) cortical, border-zone, and deep pattern.
Results: The mean (SD) volume of severe hypoperfusion was 54.6 (52.5) mL, and that of any hypoperfusion was 140.8 (81.3) mL. The HIR ranged widely, from 0.002 to 0.974, with a median of 0.35 (interquartile range 0.13-0.60). The volume of any hypoperfusion did not predict the intensity of hypoperfusion within the affected region (r = 0.10, p = 0.284). Angiographic collateral flow grade was associated with HIRs (p value for trend = 0.019) and differed among DWI lesion patterns. In multivariate analysis, diastolic pressure on admission (odds ratio 0.959, 95% CI 0.922-0.998) and DWI pattern of deep infarcts (odds ratio 18.004 compared with large cortical pattern, 95% CI 1.855-173.807) were independently associated with a low HIR.
Conclusions: The intensity of hypoperfusion within an oligemic field is largely independent of the size of the oligemia region. Predictors of lesser intensity of hypoperfusion are lower diastolic blood pressure and presence of a deep diffusion-weighted imaging lesion pattern.
Figures


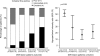
References
-
- Astrup J, Symon L, Branston NM, Lassen NA. Cortical evoked potential and extracellular K+ and H+ at critical levels of brain ischemia. Stroke 1977;8:51–57. - PubMed
-
- Donnan GA, Davis SM. Neuroimaging, the ischaemic penumbra, and selection of patients for acute stroke therapy. Lancet Neurol 2002;1:417–425. - PubMed
-
- Furlan AJ, Eyding D, Albers GW, et al. Dose escalation of desmoteplase for acute ischemic stroke (DEDAS): evidence of safety and efficacy 3 to 9 hours after stroke onset. Stroke 2006;37:1227–1231. - PubMed
-
- Hacke W, Albers G, Al-Rawi Y, et al. The desmoteplase in acute ischemic stroke trial (DIAS): a phase II MRI-based 9-hour window acute stroke thrombolysis trial with intravenous desmoteplase. Stroke 2005;36:66–73. - PubMed
-
- Albers GW, Thijs VN, Wechsler L, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging profiles predict clinical response to early reperfusion: the diffusion and perfusion imaging evaluation for understanding stroke evolution (DEFUSE) study. Ann Neurol 2006;60:508–517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
