A role for leukocyte-endothelial adhesion mechanisms in epilepsy
- PMID: 19029985
- PMCID: PMC2710311
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.1878
A role for leukocyte-endothelial adhesion mechanisms in epilepsy
Abstract
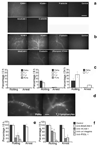
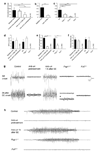
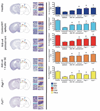
The mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of epilepsy, a chronic neurological disorder that affects approximately one percent of the world population, are not well understood. Using a mouse model of epilepsy, we show that seizures induce elevated expression of vascular cell adhesion molecules and enhanced leukocyte rolling and arrest in brain vessels mediated by the leukocyte mucin P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1, encoded by Selplg) and leukocyte integrins alpha(4)beta(1) and alpha(L)beta(2). Inhibition of leukocyte-vascular interactions, either with blocking antibodies or by genetically interfering with PSGL-1 function in mice, markedly reduced seizures. Treatment with blocking antibodies after acute seizures prevented the development of epilepsy. Neutrophil depletion also inhibited acute seizure induction and chronic spontaneous recurrent seizures. Blood-brain barrier (BBB) leakage, which is known to enhance neuronal excitability, was induced by acute seizure activity but was prevented by blockade of leukocyte-vascular adhesion, suggesting a pathogenetic link between leukocyte-vascular interactions, BBB damage and seizure generation. Consistent with the potential leukocyte involvement in epilepsy in humans, leukocytes were more abundant in brains of individuals with epilepsy than in controls. Our results suggest leukocyte-endothelial interaction as a potential target for the prevention and treatment of epilepsy.
Figures

Comment in
-
Brain inflammation initiates seizures.Nat Med. 2008 Dec;14(12):1309-10. doi: 10.1038/nm1208-1309. Nat Med. 2008. PMID: 19057551 No abstract available.
-
Leukocyte-endothelial adhesion mechanisms in epilepsy: cheers and jeers.Epilepsy Curr. 2009 Jul-Aug;9(4):118-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1535-7511.2009.01312.x. Epilepsy Curr. 2009. PMID: 19693331 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Breaching the barrier and inflaming epilepsy research.Epilepsy Curr. 2009 Sep-Oct;9(5):148-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1535-7511.2009.01324.x. Epilepsy Curr. 2009. PMID: 19826510 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Strzelczyk A, Reese JP, Dodel R, Hamer HM. Cost of epilepsy: a systematic review. Pharmacoeconomics. 2008;26:463–476. - PubMed
-
- Holmes GL. Seizure-induced neuronal injury: animal data. Neurology. 2002;59:S3–S6. - PubMed
-
- Duncan JS. Seizure-induced neuronal injury: human data. Neurology. 2002;59:S15–S20. - PubMed
-
- Vezzani A, Granata T. Brain inflammation in epilepsy: experimental and clinical evidence. Epilepsia. 2005;46:1724–1743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

