Startling mosaicism of the Y-chromosome and tandem duplication of the SRY and DAZ genes in patients with Turner Syndrome
- PMID: 19030103
- PMCID: PMC2582957
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003796
Startling mosaicism of the Y-chromosome and tandem duplication of the SRY and DAZ genes in patients with Turner Syndrome
Abstract
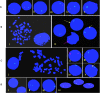
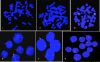
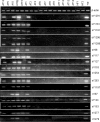
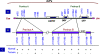
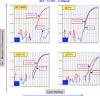
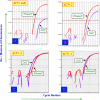
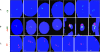
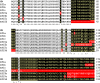
Presence of the human Y-chromosome in females with Turner Syndrome (TS) enhances the risk of development of gonadoblastoma besides causing several other phenotypic abnormalities. In the present study, we have analyzed the Y chromosome in 15 clinically diagnosed Turner Syndrome (TS) patients and detected high level of mosaicisms ranging from 45,XO:46,XY = 100:0% in 4; 45,XO:46,XY:46XX = 4:94:2 in 8; and 45,XO:46,XY:46XX = 50:30:20 cells in 3 TS patients, unlike previous reports showing 5-8% cells with Y- material. Also, no ring, marker or di-centric Y was observed in any of the cases. Of the two TS patients having intact Y chromosome in >85% cells, one was exceptionally tall. Both the patients were positive for SRY, DAZ, CDY1, DBY, UTY and AZFa, b and c specific STSs. Real Time PCR and FISH demonstrated tandem duplication/multiplication of the SRY and DAZ genes. At sequence level, the SRY was normal in 8 TS patients while the remaining 7 showed either absence of this gene or known and novel mutations within and outside of the HMG box. SNV/SFV analysis showed normal four copies of the DAZ genes in these 8 patients. All the TS patients showed aplastic uterus with no ovaries and no symptom of gonadoblastoma. Present study demonstrates new types of polymorphisms indicating that no two TS patients have identical genotype-phenotype. Thus, a comprehensive analysis of more number of samples is warranted to uncover consensus on the loci affected, to be able to use them as potential diagnostic markers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Y chromosome in Turner syndrome: review of the literature.Sao Paulo Med J. 2009 Nov;127(6):373-8. doi: 10.1590/s1516-31802009000600010. Sao Paulo Med J. 2009. PMID: 20512293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Screening for Y chromosome sequences in patients with Turner syndrome].Acta Med Port. 2002 Mar-Apr;15(2):89-100. Acta Med Port. 2002. PMID: 15524154 Portuguese.
-
Analysis of Turner syndrome patients within the Jordanian population, with a focus on four patients with Y chromosome abnormalities.Sex Dev. 2013;7(6):295-302. doi: 10.1159/000354279. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Sex Dev. 2013. PMID: 23988405
-
Detection of the SRY gene in patients with Turner Syndrome.J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2019 Apr;48(4):265-267. doi: 10.1016/j.jogoh.2019.01.012. Epub 2019 Jan 24. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2019. PMID: 30685428
-
[Y chromosome in Turner syndrome].Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2017;23(1):37-41. doi: 10.18544/PEDM-23.01.0072. Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2017. PMID: 29073306 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
The Use of Fluorescence In situ Hybridisation in the Diagnosis of Hidden Mosaicism in Egyptian Patients with Turner Syndrome.J Hum Reprod Sci. 2023 Oct-Dec;16(4):286-298. doi: 10.4103/jhrs.jhrs_128_23. Epub 2023 Dec 29. J Hum Reprod Sci. 2023. PMID: 38322635 Free PMC article.
-
Y chromosome in Turner syndrome: review of the literature.Sao Paulo Med J. 2009 Nov;127(6):373-8. doi: 10.1590/s1516-31802009000600010. Sao Paulo Med J. 2009. PMID: 20512293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutational landscape of the human Y chromosome-linked genes and loci in patients with hypogonadism.J Genet. 2015 Dec;94(4):677-87. doi: 10.1007/s12041-015-0582-1. J Genet. 2015. PMID: 26690523
-
Review of the Y chromosome, Sry and hypertension.Steroids. 2010 Nov;75(11):747-53. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2009.10.015. Epub 2009 Nov 13. Steroids. 2010. PMID: 19914267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Sry duplications on the Rattus norvegicus Y-chromosome.BMC Genomics. 2013 Nov 14;14:792. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-792. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24228692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saenger P. Turner's syndrome. Curr Ther Endocrinol Metab. 1997;6:239–243. - PubMed
-
- Gravholt CH. Epidemeological, endocrine and metabolic features in Turner's syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol. 1994;151:657–687. - PubMed
-
- Ranke MB. Turner's syndrome. Lancet. 2001;358:309–314. - PubMed
-
- Meng H, Hager K, Rivkees SA, Gruen JR. Detection of Turner syndrome using high-throughput quantitative genotyping. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(6):3419–3422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

