The barrier of hypoglycemia in diabetes
- PMID: 19033403
- PMCID: PMC2584119
- DOI: 10.2337/db08-1084
The barrier of hypoglycemia in diabetes
Figures
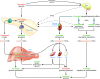

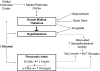
References
-
- Cryer PE: Hypoglycemia in Diabetes: Pathophysiology, Prevalence, and Prevention. American Diabetes Association, Alexandria, VA. In press
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group: The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 329 :977 –986,1993 - PubMed
-
- U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group: Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 352 :837 –853,1998 - PubMed
-
- U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group: Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 352 :854 –865,1998 - PubMed
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group: The relationship of glycemic exposure (HbA1c) to the risk of development and progression of retinopathy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes 44 :968 –983,1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

