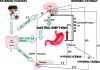
A break in the brake mechanism in diabetes: a cause of postprandial hyperglycemia
- PMID: 19033422
- PMCID: PMC2584204
- DOI: 10.2337/dc08-1694
A break in the brake mechanism in diabetes: a cause of postprandial hyperglycemia
Comment on
-
Impaired hyperglycemia-induced delay in gastric emptying in patients with type 1 diabetes deficient for islet amyloid polypeptide.Diabetes Care. 2008 Dec;31(12):2325-31. doi: 10.2337/dc07-2446. Diabetes Care. 2008. PMID: 19033417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Woerle HJ, Szoke E, Meyer C, Dostou JM, Wittlin SD, Gosmanov NR, Welle SL, Gerich JE: Mechanisms for abnormal postprandial glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 290:E67–E77, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Frank JW, Saslow SB, Camilleri M, Thomforde GM, Dinneen S, Rizza RA: Mechanism of accelerated gastric emptying of liquids and hyperglycemia in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Gastroenterology 109:755–765, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Stacher G: Diabetes and the stomach. Dig Liver Dis 32 (Suppl. 3):S253–S254, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Horowitz M, O'Donovan D, Jones KL, Feinle C, Rayner CK, Samsom M: Gastric emptying in diabetes: clinical significance and treatment. Diabet Med 19:177–194, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Camilleri M: Clinical practice. Diabetic gastroparesis. N Engl J Med 356:820–829, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical