Autophagy-induced tumor dormancy in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 19033653
- PMCID: PMC2582935
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI37667
Autophagy-induced tumor dormancy in ovarian cancer
Abstract
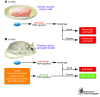
Autophagy--a process of "self-eating" that involves enzymatic digestion and recycling of cellular constituents in response to stress--contributes to both cancer cell death and survival. In this issue of the JCI, Lu et al. report that controlled induction of tumor suppressor gene aplasia Ras homolog member I (ARHI) results in autophagic cell death of human ovarian cancer cells in vitro (see the related article beginning on page 3917). However, within xenograft tumors in mice, multiple factors within the tumor microenvironment switched ARHI-induced autophagy to a mechanism of tumor cell survival, leading to tumor dormancy. Since ARHI expression is suppressed in the majority of breast and ovarian cancers but is high in premalignant lesions, ARHI-induced autophagy could be manipulated for therapeutic benefit.
Figures

Comment on
-
The tumor suppressor gene ARHI regulates autophagy and tumor dormancy in human ovarian cancer cells.J Clin Invest. 2008 Dec;118(12):3917-29. doi: 10.1172/JCI35512. Epub 2008 Nov 20. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 19033662 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

