A new model for random X chromosome inactivation
- PMID: 19036804
- PMCID: PMC2630377
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.025908
A new model for random X chromosome inactivation
Abstract
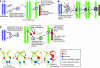
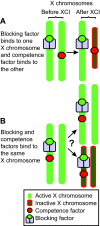
X chromosome inactivation (XCI) reduces the number of actively transcribed X chromosomes to one per diploid set of autosomes, allowing for dosage equality between the sexes. In eutherians, the inactive X chromosome in XX females is randomly selected. The mechanisms for determining both how many X chromosomes are present and which to inactivate are unknown. To understand these mechanisms, researchers have created X chromosome mutations and transgenes. Here, we introduce a new model of X chromosome inactivation that aims to account for the findings in recent studies, to promote a re-interpretation of existing data and to direct future experiments.
Figures




References
-
- Augui, S., Filion, G. J., Huart, S., Nora, E., Guggiari, M., Maresca, M., Stewart, A. F. and Heard, E. (2007). Sensing X chromosome pairs before X inactivation via a novel X-pairing region of the Xic. Science 318, 1632-1636. - PubMed
-
- Bacher, C. P., Guggiari, M., Brors, B., Augui, S., Clerc, P., Avner, P., Eils, R. and Heard, E. (2006). Transient colocalization of X-inactivation centres accompanies the initiation of X inactivation. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 293-299. - PubMed
-
- Borsani, G., Tonlorenzi, R., Simmler, M. C., Dandolo, L., Arnaud, D., Capra, V., Grompe, M., Pizzuti, A., Muzny, D., Lawrence, C. et al. (1991). Characterization of a murine gene expressed from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 351, 325-329. - PubMed
-
- Brockdorff, N., Ashworth, A., Kay, G. F., Cooper, P., Smith, S., McCabe, V. M., Norris, D. P., Penny, G. D., Patel, D. and Rastan, S. (1991). Conservation of position and exclusive expression of mouse Xist from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 351, 329-331. - PubMed
-
- Brown, C. J., Ballabio, A., Rupert, J. L., Lafreniere, R. G., Grompe, M., Tonlorenzi, R. and Willard, H. F. (1991a). A gene from the region of the human X inactivation centre is expressed exclusively from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 349, 38-44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

