Beta-catenin is a mediator of the response of fibroblasts to irradiation
- PMID: 19036807
- PMCID: PMC2631337
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080576
Beta-catenin is a mediator of the response of fibroblasts to irradiation
Abstract
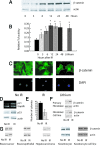
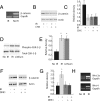
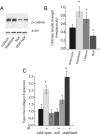
Radiation causes soft tissue complications that include fibrosis and deficient wound healing. beta-Catenin, a key component in the canonical Wnt-signaling pathway, is activated in fibrotic processes and wound repair and, as such, could play a role in mediating cellular responses to irradiation. beta-Catenin can form a transcriptionally active complex with members of the Tcf family. A reporter mouse model, in addition to human cell cultures, was used to demonstrate that ionizing radiation activates beta-catenin-mediated, Tcf-dependent transcription both in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, radiation activates beta-catenin via a Wnt-mediated mechanism, as in the presence of dickkopf-1, an inhibitor of Wnt receptor activation, beta-catenin levels did not increase after irradiation. Fibroblast cell cultures were derived from mice expressing either null or stabilized beta-catenin alleles. Cells expressing stabilized beta-catenin alleles had a higher proliferation rate and formed more colony-forming units than wild-type or null cells after irradiation. Wound healing was studied in these same mice after irradiation. There was a positive correlation between the tensile strength of the wound, the expression levels of type 1 collagen in the skin, and beta-catenin levels. Mice treated with lithium showed increased beta-catenin levels and increased wound strength. beta-Catenin mediates the effects of ionizing radiation in fibroblasts, and its modulation has the potential to decrease the severity of radiation-induced soft tissue complications.
Figures


References
-
- Nasonova E, Fussel K, Berger S, Gudowska-Nowak E, Ritter S. Cell cycle arrest and aberration yield in normal human fibroblasts. I. Effects of X-rays and 195 MeV u(-1) C ions. Int J Radiat Biol. 2004;80:621–634. - PubMed
-
- van Kampen M, Eble MJ, Lehnert T, Bernd L, Jensen K, Hensley F, Krempien R, Wannenmacher M. Correlation of intraoperatively irradiated volume and fibrosis in patients with soft-tissue sarcoma of the extremities. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;51:94–99. - PubMed
-
- Rodemann HP, Bamberg M. Cellular basis of radiation-induced fibrosis. Radiother Oncol. 1995;35:83–90. - PubMed
-
- O'Sullivan B, Levin W. Late radiation-related fibrosis: pathogenesis, manifestations, and current management. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2003;13:274–289. - PubMed
-
- Gavert N, Ben-Ze'ev A. Beta-catenin signaling in biological control and cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2007;102:820–828. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

