Broad-spectrum inhibition of retroviral and filoviral particle release by tetherin
- PMID: 19036818
- PMCID: PMC2643743
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02211-08
Broad-spectrum inhibition of retroviral and filoviral particle release by tetherin
Abstract
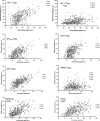
The expression of many putative antiviral genes is upregulated when cells encounter type I interferon (IFN), but the actual mechanisms by which many IFN-induced gene products inhibit virus replication are poorly understood. A recently identified IFN-induced antiretroviral protein, termed tetherin (previously known as BST-2 or CD317), blocks the release of nascent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) particles from infected cells, and an HIV-1 accessory protein, Vpu, acts as a viral antagonist of tetherin. Here, we show that tetherin is capable of blocking not only the release of HIV-1 particles but also the release of particles assembled using the major structural proteins of a variety of prototype retroviruses, including members of the alpharetrovirus, betaretrovirus, deltaretrovirus, lentivirus, and spumaretrovirus families. Moreover, we show that the release of particles assembled using filovirus matrix proteins from Marburg virus and Ebola virus is also sensitive to inhibition by tetherin. These findings indicate that tetherin is a broadly specific inhibitor of enveloped particle release, and therefore, inhibition is unlikely to require specific interactions with viral proteins. Nonetheless, tetherin colocalized with nascent virus-like particles generated by several retroviral and filoviral structural proteins, indicating that it is present at, or recruited to, sites of particle assembly. Overall, tetherin is potentially active against many enveloped viruses and likely to be an important component of the antiviral innate immune defense.
Figures
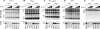
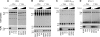

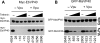

References
-
- Barker, C. S., J. Pickel, M. Tainsky, and E. Hunter. 1986. Molecular cloning of the Mason-Pfizer monkey virus genome: biological characterization of genome length clones and molecular comparisons to other retroviruses. Virology 153201-214. - PubMed
-
- Bieniasz, P. D. 2004. Intrinsic immunity: a front-line defense against viral attack. Nat. Immunol. 51109-1115. - PubMed
-
- Blasius, A. L., E. Giurisato, M. Cella, R. D. Schreiber, A. S. Shaw, and M. Colonna. 2006. Bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 is a specific marker of type I IFN-producing cells in the naive mouse, but a promiscuous cell surface antigen following IFN stimulation. J. Immunol. 1773260-3265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

