Structural and functional requirements for activity of the Tim9-Tim10 complex in mitochondrial protein import
- PMID: 19037098
- PMCID: PMC2633397
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e08-09-0903
Structural and functional requirements for activity of the Tim9-Tim10 complex in mitochondrial protein import
Abstract
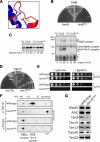
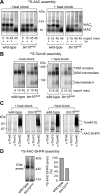
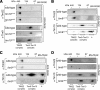
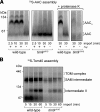
The Tim9-Tim10 complex plays an essential role in mitochondrial protein import by chaperoning select hydrophobic precursor proteins across the intermembrane space. How the complex interacts with precursors is not clear, although it has been proposed that Tim10 acts in substrate recognition, whereas Tim9 acts in complex stabilization. In this study, we report the structure of the yeast Tim9-Tim10 hexameric assembly determined to 2.5 A and have performed mutational analysis in yeast to evaluate the specific roles of Tim9 and Tim10. Like the human counterparts, each Tim9 and Tim10 subunit contains a central loop flanked by disulfide bonds that separate two extended N- and C-terminal tentacle-like helices. Buried salt-bridges between highly conserved lysine and glutamate residues connect alternating subunits. Mutation of these residues destabilizes the complex, causes defective import of precursor substrates, and results in yeast growth defects. Truncation analysis revealed that in the absence of the N-terminal region of Tim9, the hexameric complex is no longer able to efficiently trap incoming substrates even though contacts with Tim10 are still made. We conclude that Tim9 plays an important functional role that includes facilitating the initial steps in translocating precursor substrates into the intermembrane space.
Figures


References
-
- Allen S., Balabanidou V., Sideris D. P., Lisowsky T., Tokatlidis K. Erv1 mediates the Mia40-dependent protein import pathway and provides a functional link to the respiratory chain by shuttling electrons to cytochrome c. J. Mol. Biol. 2005;353:937–944. - PubMed
-
- Baker M. J., Frazier A. E., Gulbis J. M., Ryan M. T. Mitochondrial protein-import machinery: correlating structure with function. Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17:456–464. - PubMed
-
- Brunger A. T., et al. Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1998;54:905–921. - PubMed
-
- Chacinska A., et al. Mitochondrial presequence translocase: switching between TOM tethering and motor recruitment involves Tim21 and Tim17. Cell. 2005;120:817–829. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

