HER-2-directed, small-molecule antagonists
- PMID: 19037833
- PMCID: PMC3031872
HER-2-directed, small-molecule antagonists
Abstract
Inactivation of the human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER-2) tyrosine kinase holds significant promise as a cancer treatment hypothesis, making it a high-value target for drug discovery. Screening and structure-based efforts have led to the development of several classes of ATP analog inhibitors of the HER-2 tyrosine kinase. These efforts have been further enhanced by detailed structural information regarding its sibling kinase, the EGF receptor, and structural properties that can be exploited to confer activity and even selectivity toward HER-2 kinase. Signaling and structural studies also suggest a critical involvement of the kinase inactive HER-3 in the regulation of HER-2, creating unique challenges in the efforts to inactivate the latter.
Figures



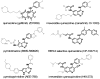


References
-
- Berger MB, Mendrola JM, Lemmon MA. ErbB3/HER3 does not homodimerize upon neuregulin binding at the cell surface. FEBS Lett. 2004;569(1–3):332–336. - PubMed
-
- Tzahar E, Waterman H, Chen X, Levkowitz G, Karunagaran D, Lavi S, Ratzkin BJ, Yarden Y. A hierarchical network of interreceptor interactions determines signal transduction by Neu differentiation factor/neuregulin and epidermal growth factor. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 1996;16:5276–5287. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Gureasko J, Shen K, Cole PA, Kuriyan J. An allosteric mechanism for activation of the kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell. 2006;125(6):1137–1149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
