Striatal plasticity and basal ganglia circuit function
- PMID: 19038213
- PMCID: PMC2724179
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.11.005
Striatal plasticity and basal ganglia circuit function
Abstract
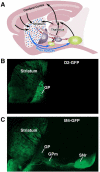
The dorsal striatum, which consists of the caudate and putamen, is the gateway to the basal ganglia. It receives convergent excitatory afferents from cortex and thalamus and forms the origin of the direct and indirect pathways, which are distinct basal ganglia circuits involved in motor control. It is also a major site of activity-dependent synaptic plasticity. Striatal plasticity alters the transfer of information throughout basal ganglia circuits and may represent a key neural substrate for adaptive motor control and procedural memory. Here, we review current understanding of synaptic plasticity in the striatum and its role in the physiology and pathophysiology of basal ganglia function.
Figures
References
-
- Albin RL, Young AB, Penney JB. The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci. 1989;12:366–375. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GE, Crutcher MD. Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci. 1990;13:266–271. - PubMed
-
- Aouizerate B, Guehl D, Cuny E, Rougier A, Bioulac B, Tignol J, Burbaud P. Pathophysiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder: a necessary link between phenomenology, neuropsychology, imagery and physiology. Prog. Neurobiol. 2004;72:195–221. - PubMed
-
- Aravanis AM, Wang LP, Zhang F, Meltzer LA, Mogri MZ, Schneider MB, Deisseroth K. An optical neural interface: in vivo control of rodent motor cortex with integrated fiberoptic and optogenetic technology. J. Neural Eng. 2007;4:S143–S156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

