A biological function for the neuronal activity-dependent component of Bdnf transcription in the development of cortical inhibition
- PMID: 19038219
- PMCID: PMC2873221
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.09.024
A biological function for the neuronal activity-dependent component of Bdnf transcription in the development of cortical inhibition
Abstract
Neuronal activity-regulated gene expression has been suggested to be an important mediator of long-lasting, experience-dependent changes in the nervous system, but the activity-dependent component of gene transcription has never been selectively isolated and tested for its functional significance. Here, we demonstrate that introduction of a subtle knockin mutation into the mouse Bdnf gene that blocks the ability of the activity-regulated factor CREB to bind Bdnf promoter IV results in an animal in which the sensory experience-dependent induction of Bdnf expression is disrupted in the cortex. Neurons from these animals form fewer inhibitory synapses, have fewer spontaneous inhibitory quantal events, and exhibit reduced expression of inhibitory presynaptic markers in the cortex. These results indicate a specific requirement for activity-dependent Bdnf expression in the development of inhibition in the cortex and demonstrate that the activation of gene expression in response to experience-driven neuronal activity has important biological consequences in the nervous system.
Figures



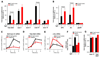
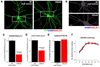
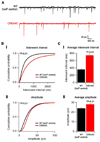


Comment in
-
Biological functions of activity-dependent transcription revealed.Neuron. 2008 Nov 26;60(4):523-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.11.008. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 19038208 Review.
References
-
- Abidin I, Kohler T, Weiler E, Zoidl G, Eysel UT, Lessmann V, Mittmann T. Reduced presynaptic efficiency of excitatory synaptic transmission impairs LTP in the visual cortex of BDNF-heterozygous mice. Eur J Neurosci. 2006;24:3519–3531. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP, Sheng M, Lau LF, Greenberg ME. Growth factors and membrane depolarization activate distinct programs of early response gene expression: dissociation of fos and jun induction. Genes Dev. 1989;3:304–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

