Reliability of MRI-derived cortical and subcortical morphometric measures: effects of pulse sequence, voxel geometry, and parallel imaging
- PMID: 19038349
- PMCID: PMC2739882
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.037
Reliability of MRI-derived cortical and subcortical morphometric measures: effects of pulse sequence, voxel geometry, and parallel imaging
Abstract
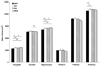
Advances in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have contributed greatly to the study of neurodegenerative processes, psychiatric disorders, and normal human development, but the effect of such improvements on the reliability of downstream morphometric measures has not been extensively studied. We examined how MRI-derived neurostructural measures are affected by three technological advancements: parallel acceleration, increased spatial resolution, and the use of a high bandwidth multiecho sequence. Test-retest data were collected from 11 healthy participants during 2 imaging sessions occurring approximately 2 weeks apart. We acquired 4 T1-weighted MP-RAGE sequences during each session: a non-accelerated anisotropic sequence (MPR), a non-accelerated isotropic sequence (ISO), an accelerated isotropic sequence (ISH), and an accelerated isotropic high bandwidth multiecho sequence (MEM). Cortical thickness and volumetric measures were computed for each sequence to assess test-retest reliability and measurement bias. Reliability was extremely high for most measures and similar across imaging parameters. Significant measurement bias was observed, however, between MPR and all isotropic sequences for all cortical regions and some subcortical structures. These results suggest that these improvements in MRI acquisition technology do not compromise data reproducibility, but that consistency should be maintained in choosing imaging parameters for structural MRI studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
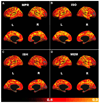
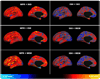
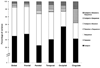
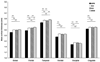

References
-
- Carlson JW, Minemura T. Imaging time reduction through multiple receiver coil data acquisition and image reconstruction. Magn. Reson. Med. 1993;29:681–687. - PubMed
-
- Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI. Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage. 1999;9:179–194. - PubMed
-
- Deichmann R, Good CD, Josephs O, Ashburner J, Turner R. Optimization of 3-D MP-RAGE sequences for structural brain imaging. Neuroimage. 2000;12:112–127. - PubMed
-
- Desikan RS, Segonne F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D, Buckner RL, Dale AM, Maguire RP, Hyman BT, Albert MS, Killiany RJ. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage. 2006;31:968–980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

