A COPI coat subunit interacts directly with an early-Golgi localized Arf exchange factor
- PMID: 19039328
- PMCID: PMC2613206
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2008.221
A COPI coat subunit interacts directly with an early-Golgi localized Arf exchange factor
Abstract
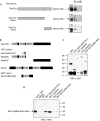
Arf (ADP-ribosylation factor) family small G proteins are crucial regulators of intracellular transport. The active GTP-bound form of Arf interacts with a set of proteins--effectors--which mediate the downstream signalling events of Arf activation. A well-studied class of Arf1 effectors comprises the coat complexes, such as the cis-Golgi-localized COPI (coat protein complex I) coat, and trans-Golgi network-endosomal clathrin coats. At least five different coats require Arf1-GTP to localize to organelle membranes. How a single Arf protein recruits different coat complexes to distinct membrane sites raises the question of how specificity is achieved. Here, we propose a molecular mechanism of this specificity for the COPI coat by showing a direct and specific interaction between a COPI subunit and a cis-Golgi localized subfamily of Arf guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) that takes place independently of Arf1 activation. In this way, a specific output on Arf1 activation can be programmed before the exchange reaction by the GEF itself.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bethune J, Wieland F, Moelleken J (2006) COPI-mediated transport. J Membr Biol 211: 65–79 - PubMed
-
- Bonifacino JS, Lippincott-Schwartz J (2003) Coat proteins: shaping membrane transport. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 409–414 - PubMed
-
- Casanova JE (2007) Regulation of arf activation: the sec7 family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Traffic 8: 1476–1485 - PubMed
-
- Gillingham AK, Munro S (2007) The small G proteins of the Arf family and their regulators. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23: 579–611 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

