Lipopolysaccharide impairs blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein function in mice through prostaglandin- and nitric oxide-independent pathways
- PMID: 19039663
- PMCID: PMC2802264
- DOI: 10.1007/s11481-008-9138-y
Lipopolysaccharide impairs blood-brain barrier P-glycoprotein function in mice through prostaglandin- and nitric oxide-independent pathways
Abstract
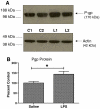
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is a brain-to-blood efflux system that controls the ability of many drugs and endogenous substances to access the brain. In vitro work has shown that inflammatory states mediated through lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha first impair and then stimulate P-gp activity. Here, we determined whether LPS can affect P-gp function in vivo. Mice treated with a single intraperitoneal injection of LPS (3 mg/kg) showed an inhibition of P-gp function. As assessed by brain perfusion, inhibition began 18 h after LPS administration and lasted until 36 h after administration. P-gp protein was increased by 44%, consistent with P-gp inhibition occurring through post-translational mechanisms. Unlike other effects of LPS on blood-brain barrier function, neither nitric oxide nor prostaglandin inhibition had an effect. We conclude that induction of proinflammatory states as exemplified by LPS treatment can inhibit P-gp function in vivo at the blood-brain barrier.
Figures


References
-
- Aquilante CL, Letrent SP, Pollack GM, Brouwer KL. Increased brain P-glycoprotein in morphine tolerant rats. Life Sci. 2000;66:PL47–PL51. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Brennan JM, Vallance KL. Adsorptive endocytosis of HIV-1gp120 by blood–brain barrier is enhanced by lipopolysaccharide. Exp Neurol. 1999;156:165–171. - PubMed
-
- Bauer B, Hartz AMS, Miller DS. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and endothelin-1 increase P-glycoprotein expression and transport activity at the blood–brain barrier. Mol Pharmacol. 2007;71:667–675. - PubMed
-
- Begley DJ. ABC transporters and the blood–brain barrier. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10:1295–1312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

