TC-5214 (S-(+)-mecamylamine): a neuronal nicotinic receptor modulator with antidepressant activity
- PMID: 19040552
- PMCID: PMC6494058
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2008.00054.x
TC-5214 (S-(+)-mecamylamine): a neuronal nicotinic receptor modulator with antidepressant activity
Abstract
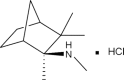
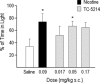
Both clinical and preclinical data support a potential therapeutic benefit of modulating the activity of CNS neuronal nicotinic receptors (NNRs) to treat depression and anxiety disorders. Based on the notion that the depressive states involve hypercholinergic tone, we have examined the potential palliative role of NNR antagonism in these disorders, using TC-5214 (S-(+) enantiomer of mecamylamine), a noncompetitive NNR antagonist. TC-5214 demonstrated positive effects in a number of animal models of depression and anxiety. TC-5214 was active in the forced swim test in rats (minimum effective dose (MED)=3 mg/kg i.p.), a classical depression model. It was also active in the behavioral despair test in mice (0.1-3.0 mg/kg i.p.), another model of depression. In the social interaction paradigm in rats, a model of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), TC-5214 was active at a dose of 0.05 mg/kg s.c. In the light/dark chamber paradigm in rats, a model of GAD and phobia, TC-5214 was also active at a dose of 0.05 mg/kg s.c. Although TC-5214 shows modest selectivity among NNR subtypes, the antidepressant and anxiolytic effects seen in these studies are likely attributable to antagonist effects at the alpha4beta2 NNRs. This is supported by the observation of similar effects with alpha4beta2-selective partial agonists such as cytisine and with alpha4beta2-selective antagonists such as TC-2216. TC-5214 was well tolerated in acute and chronic toxicity studies in mice, rats, and dogs, showed no mutagenicity and displayed safety pharmacology, pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles appropriate for therapeutic development. Overall, the results support a novel nicotinic cholinergic antagonist mechanism for antidepressant and anxiolytic effects and highlight the potential of NNR antagonists such as TC-5214 as therapeutics for the treatment of anxiety and depression.
Figures



References
-
- Janowsky D, El‐Yousef MK, Davis JM. Acetylcholine and depression. Psychosomatic Med 1974;36:248–257. - PubMed
-
- Janowsky DS, Risch SC. Cholinomimetic and anticholinergic drugs used to investigate and acetylcholine hypothesis of affective disorders and stress. Drug Development Res 1984;4:125–142.
-
- Shytle RD, Silver AA, Lukas RJ, Newman MB, Sheehan DV, Sanberg PR. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors as targets for antidepressants. Mol Psychiatry 2002;7:525–535. - PubMed
-
- Picciotto MR, Brunzell DH, Caldarone BJ. Effect of nicotine and nicotinic receptors on anxiety and depression. Neuroreport 2002;13:1097–1106. - PubMed
-
- Fryer JD, Lukas RJ. Antidepressants noncompetitively inhibit nicotinic acetylcholine receptor function. J Neurochem 1999;72:1117–1124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

