Arena3D: visualization of biological networks in 3D
- PMID: 19040715
- PMCID: PMC2637860
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-0509-2-104
Arena3D: visualization of biological networks in 3D
Abstract
Background: Complexity is a key problem when visualizing biological networks; as the number of entities increases, most graphical views become incomprehensible. Our goal is to enable many thousands of entities to be visualized meaningfully and with high performance.
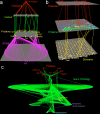
Results: We present a new visualization tool, Arena3D, which introduces a new concept of staggered layers in 3D space. Related data--such as proteins, chemicals, or pathways--can be grouped onto separate layers and arranged via layout algorithms, such as Fruchterman-Reingold, distance geometry, and a novel hierarchical layout. Data on a layer can be clustered via k-means, affinity propagation, Markov clustering, neighbor joining, tree clustering, or UPGMA ('unweighted pair-group method with arithmetic mean'). A simple input format defines the name and URL for each node, and defines connections or similarity scores between pairs of nodes. The use of Arena3D is illustrated with datasets related to Huntington's disease.
Conclusion: Arena3D is a user friendly visualization tool that is able to visualize biological or any other network in 3D space. It is free for academic use and runs on any platform. It can be downloaded or lunched directly from http://arena3d.org. Java3D library and Java 1.5 need to be pre-installed for the software to run.
Figures
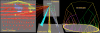
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

