Usefulness of pulsed arterial spin labeling MR imaging in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy
- PMID: 19041041
- PMCID: PMC2597620
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2008.08.001
Usefulness of pulsed arterial spin labeling MR imaging in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy
Abstract
Purpose: Arterial spin labeling (ASL) is a developing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) method for noninvasive measurement of cerebral blood flow (CBF). The purpose of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of ASL for detecting interictal temporal hypoperfusion in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE). ASL-derived CBF measurements were compared with those derived from H(2)(15)O positron emission tomography (PET).
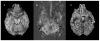
Methods: 11 normal controls and 10 patients with medically intractable TLE were studied. Pulsed ASL (PASL) with quantitative imaging of perfusion using a single subtraction, second version (QUIPSS II) was performed in all subjects and H(2)(15)O PET was performed in patients. Regional CBF values in the mesial and lateral temporal lobes were measured utilizing quantitative analysis of perfusion images. A perfusion asymmetry index (AI) was calculated for each region.
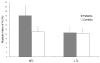
Results: In patients, mean CBF in the mesial temporal lobe was not significantly different between PASL and H(2)(15)O PET, and ipsilateral mesial temporal CBF was lower than contralateral CBF with both techniques. PASL detected significant mesial temporal perfusion asymmetry agreeing with EEG laterality in four patients. H(2)(15)O PET found ipsilateral interictal hypoperfusion in three. Both scans found unilateral hypoperfusion in one patient with bilateral EEG discharges.
Conclusions: Pulsed ASL may be a promising approach to detecting interictal hypoperfusion in TLE. This method has potential as a clinical alternative to H(2)(15)O PET due to noninvasiveness and easy accessibility.
Figures
References
-
- Alsop DC, Connelly A, Duncan JS, Hufnagel A, Pierpaoli C, Rugg-Gunn FJ. Diffusion and Perfusion MRI in Epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2002;43:69–77.
-
- Barbier EL, Lamalle L, Decorps M. Methodology of brain perfusion imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2001;13:496–520. - PubMed
-
- Buxton RB, Frank LR, Wong EC, Siewert B, Warach S, Edelman RR. A general kinetic model for quantitative perfusion imaging with arterial spin labeling. Magn Reson Med. 1998;40:383–396. - PubMed
-
- Buxton RB. Quantifying CBF with arterial spin labeling. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2005;22:723–726. - PubMed
-
- Calamante F, Thomas DL, Pell GS, Wiersma J, Turner R. Measuring cerebral blood flow using magnetic resonance imaging techniques. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19:701–735. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

