Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia: impact of donor source on survival
- PMID: 19041062
- PMCID: PMC5477848
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2008.09.021
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia: impact of donor source on survival
Abstract
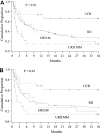
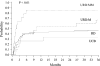
We studied the relative impact of donor source on outcomes following myeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for adult patients with acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). In this single center study, 138 patients aged 18-61 (median 31) years underwent myeloablative conditioning followed by allogeneic HSCT. Stem cell source was an HLA matched related donor (MRD) in 90, HLA matched unrelated donor (URD:M) in 15, HLA mismatched unrelated donor (URD:MM) in 14, and HLA 0-2 (A, B, DRB1) mismatched umbilical cord blood (UCB) in 19 patients. At the time of HSCT, 70 patients were in first clinical remission (CR1), 57 in CR2, and 11 in > or =CR3. Twenty-one patients had T-lineage disease; 43 patients (31%) had high-risk cytogenetics of either t(9;22) (n = 33), t(4;11) or t(1,19) abnormalities, with the remainder (69%) having normal cytogenetics. White blood cell count (WBC) > or =30 x 10(9)/L at diagnosis was documented in 33%. Demographics and disease characteristics were similar in all 4 groups except all UCB recipients were treated since 1996 and received growth factors. Overall survival (OS) at 3 years for the UCB group was 66% (95% confidence interval [CI] 44%-89%) compared to 27% (95% CI 17%-36%) in the MRD group, and only 13% (95% CI 0%-31%) and 14% (95% CI 0%-33%) in the URD:M and URD:MM groups, respectively. Similarly leukemia free survival (LFS) at 3 years was better in the UCB group at 61% (95% CI 38%-84%) than 27% (95% CI 18%-36%) in the MRD and only 13% (95% CI 0%-31%) in the URD:M group and 14% (95%CI 0%-33%) in URD:MM group. Relapse rates at 3 years were 5% (95% CI 0%-15%) in the UCB group compared to 26% (95% CI 16%-35%) in the MRD, 20% (95% CI 1%-39%) in the URD:M groups, and 0% in the URD:MM groups. Transplant-related mortality (TRM) at 3 years was the lowest in the UCB group at 34% and higher in the other donor groups: MRD 47%, URD:M 67%, and URD:MM 86%. In multiple regression analysis, 5 independent risk factors were significantly associated with poorer OS and LFS: use of URD:MM (relative risk [RR] 2.5, 95% CI, 1.2-5.1, P = .01), > or =CR3 at HSCT (RR 3.5, 95% CI, 1.2-9.6, P = .02), WBC > or =30 x 10(9)/l (RR 1.9, 95% CI, 1.2-3.0, P = .01) at diagnosis, recipient and donor (R/D) cytomegalovirus (CMV) seropositive (RR 3.8, 95% CI, 2.0-7.4, P < .01), and > or =2 induction regimens to achieve initial CR (RR 3.5, 95% CI, 1.2-9.6, P = .02). Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) was associated with improved LFS (RR 0.4, 95% CI, 0.2-0.6, P < .01). When compared with URD:M, OS with UCB was better (RR 0.3, 95% CI, 0.1-0.7, P = .01), supporting the use of UCB as an alternative stem cell source for adults with ALL.
Figures
References
-
- Goldstone AH, Richards SM, Lazarus HM, et al. In adults with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the greatest benefit is achieved from a matched sibling allogeneic transplantation in first complete remission, and an autologous transplantation is less effective than conventional consolidation/maintenance chemotherapy in all patients: final results of the International ALL Trial (MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993) Blood. 2008;111:1827–18331. - PubMed
-
- Grewal SS, Barker JN, Davies SM, et al. Unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation: marrow or umbilical cord blood? Blood. 2003;101:4233–4244. - PubMed
-
- Rocha V, Wagner JE, Jr, Sobocinski KA, et al. Graft-versus-host disease in children who have received a cord-blood or bone marrow transplant from an HLA-identical sibling. Eurocord and International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry Working Committee on Alternative Donor and Stem Cell Sources. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1846–1854. - PubMed
-
- Rocha V, Cornish J, Sievers EL, et al. Comparison of outcomes of unrelated bone marrow and umbilical cord blood transplants in children with acute leukemia. Blood. 2001;97:2962–2971. - PubMed
-
- Barker JN, Davies SM, DeFor T, et al. Survival after transplantation of unrelated donor umbilical cord blood is comparable to that of human leukocyte antigen-matched unrelated donor bone marrow: results of a matched-pair analysis. Blood. 2001;97:2957–2961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous