SIRT1 redistribution on chromatin promotes genomic stability but alters gene expression during aging
- PMID: 19041753
- PMCID: PMC2853975
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.025
SIRT1 redistribution on chromatin promotes genomic stability but alters gene expression during aging
Abstract
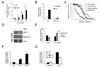
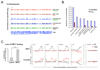
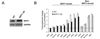
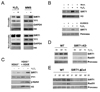
Genomic instability and alterations in gene expression are hallmarks of eukaryotic aging. The yeast histone deacetylase Sir2 silences transcription and stabilizes repetitive DNA, but during aging or in response to a DNA break, the Sir complex relocalizes to sites of genomic instability, resulting in the desilencing of genes that cause sterility, a characteristic of yeast aging. Using embryonic stem cells, we show that mammalian Sir2, SIRT1, represses repetitive DNA and a functionally diverse set of genes across the mouse genome. In response to DNA damage, SIRT1 dissociates from these loci and relocalizes to DNA breaks to promote repair, resulting in transcriptional changes that parallel those in the aging mouse brain. Increased SIRT1 expression promotes survival in a mouse model of genomic instability and suppresses age-dependent transcriptional changes. Thus, DNA damage-induced redistribution of SIRT1 and other chromatin-modifying proteins may be a conserved mechanism of aging in eukaryotes.
Figures
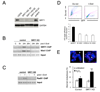
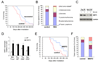
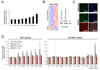
Comment in
-
Aging: a sirtuin shake-up?Cell. 2008 Nov 28;135(5):797-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.008. Cell. 2008. PMID: 19041745
References
-
- Araki T, Sasaki Y, Milbrandt J. Increased nuclear NAD biosynthesis and SIRT1 activation prevent axonal degeneration. Science. 2004;305:1010–1013. - PubMed
-
- Bahar R, Hartmann CH, Rodriguez KA, Denny AD, Busuttil RA, Dolle ME, Calder RB, Chisholm GB, Pollock BH, Klein CA, Vijg J. Increased cell-to-cell variation in gene expression in ageing mouse heart. Nature. 2006;441:1011–1014. - PubMed
-
- Baur JA, Sinclair DA. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:493–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01AG020681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 GM073894/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM068072/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG027916/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- GM 073894/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047188/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS047188/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM068072/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019719/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG028730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG19719/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

