Delivery of Interferon-gamma by an adenovirus vector blocks herpes simplex virus Type 1 reactivation in vitro and in vivo independent of RNase L and double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase pathways
- PMID: 19042034
- PMCID: PMC2626643
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.10.008
Delivery of Interferon-gamma by an adenovirus vector blocks herpes simplex virus Type 1 reactivation in vitro and in vivo independent of RNase L and double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase pathways
Abstract
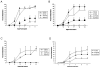
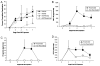
HSV-1 is a significant human pathogen that can result in the loss of sight as a result of episodic reactivation of latent virus from sensory ganglion neurons. In this study the potential efficacy of anti-viral cytokine expression in preventing latent virus reactivation was investigated. Both type I (IFN-beta) and type II (IFN-gamma) IFN transgene expression following transduction of trigeminal ganglion explant cultures significantly reduced the incident of HSV-1 reactivation that in the case of IFN-beta was dependent on the presence of double stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase and RNase L. In vivo, expression of the IFN-gamma but not IFN-beta transgene significantly delayed and reduced the frequency of reactivation of latent mice exposed to UV light without discernable inflammation. This result is the first report that demonstrates the ability to block reactivation using an ectopic cytokine expression system and warrants further exploration as a means to prevent HSV-1 reactivation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The murine double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR and the murine 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase-dependent RNase L are required for IFN-beta-mediated resistance against herpes simplex virus type 1 in primary trigeminal ganglion culture.Virology. 2003 Aug 15;313(1):126-35. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(03)00298-8. Virology. 2003. PMID: 12951027
-
Critical role for the oligoadenylate synthetase/RNase L pathway in response to IFN-beta during acute ocular herpes simplex virus type 1 infection.J Immunol. 2005 Jul 15;175(2):1100-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.2.1100. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16002711
-
An M2 Rather than a TH2 Response Contributes to Better Protection against Latency Reactivation following Ocular Infection of Naive Mice with a Recombinant Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Expressing Murine Interleukin-4.J Virol. 2018 Apr 27;92(10):e00051-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00051-18. Print 2018 May 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29491152 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of deficiency of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase, PKR, on antiviral resistance in the presence or absence of ribonuclease L: HSV-1 replication is particularly sensitive to deficiency of the major IFN-mediated enzymes.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2000 Jul;20(7):653-9. doi: 10.1089/107999000414835. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2000. PMID: 10926208
-
Mechanisms employed by herpes simplex virus 1 to inhibit the interferon response.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009 Sep;29(9):599-607. doi: 10.1089/jir.2009.0074. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009. PMID: 19694546 Review.
Cited by
-
Defining nervous system susceptibility during acute and latent herpes simplex virus-1 infection.J Neuroimmunol. 2017 Jul 15;308:43-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2017.02.020. Epub 2017 Mar 8. J Neuroimmunol. 2017. PMID: 28302316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recurrent herpetic stromal keratitis in mice, a model for studying human HSK.J Vis Exp. 2012 Dec 18;(70):e4276. doi: 10.3791/4276. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 23271160 Free PMC article.
-
IL-29/IL-28A suppress HSV-1 infection of human NT2-N neurons.J Neurovirol. 2011 Jun;17(3):212-9. doi: 10.1007/s13365-011-0031-8. Epub 2011 Apr 16. J Neurovirol. 2011. PMID: 21499846 Free PMC article.
-
Case Report: Rapid Recognition and Immune Modulation of Secondary HLH Due to Disseminated HSV Infection.Front Pediatr. 2021 Jul 2;9:681055. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.681055. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34277520 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological control of herpes simplex virus infections.J Neurovirol. 2013 Aug;19(4):328-45. doi: 10.1007/s13365-013-0189-3. Epub 2013 Aug 14. J Neurovirol. 2013. PMID: 23943467 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Al-khatib K, Williams BRG, Silverman RH, Halford W, Carr DJJ. The murine double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR and the murine 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase-dependent RNase L are required for IFN-β-mediated resistance against herpes simplex virus type 1 in primary trigeminal ganglion culture. Virology. 2003;313:126–135. - PubMed
-
- Austin BA, James C, Silverman RH, Carr DJJ. Critical role for the oligoadenylate synthetase/RNase L pathway in response to IFN-β during acute ocular herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. J. Immunol. 2005;175:1100–1106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

