The expression and localization of inhibin isotypes in mouse testis during postnatal development
- PMID: 19043308
- PMCID: PMC2811774
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2008.9.4.345
The expression and localization of inhibin isotypes in mouse testis during postnatal development
Abstract
Inhibin, which is important for normal gonadal function, acts on the pituitary gonadotropins to suppress folliclestimulating hormone (FSH) secretion. The level and cellular localization of the inhibin isotypes, alpha, betaA and betaB, in the testis of mice were examined during postnatal development in order to determine if inhibin expression is related to testicular maturation. Mouse testes were sampled on postnatal days (PNDs) 1, 3, 6, 18, 48 and 120, and analyzed by Western blotting and immunofluorescence. Western blot analysis showed very low levels of inhibin alpha, betaA and betaB expression in the testes at days 1 to 6 after birth. The levels then increased gradually from PND 18 to 48-120, and there were significant peaks at PND 48. Inhibin alpha, betaA and betaB were detected in testicular cells during postnatal development using immunohistochemistry. The immunoreactivity of inhibin alpha was rarely observed in testicular cells during PND 1 to 6, or in the cytoplasmic process of Sertoli cells surrounding the germ cells and interstitial cells during PND 18 to 120. Inhibin betaA and betaB immunoreactivity was rarely observed in the testis from PND 1 to 6. On the other hand, it was observed in some spermatogonial cells, as well as in the interstitial space between PND 48 and PND 120. We conclude that the expression of inhibin isotypes increases progressively in the testis of mice with increasing postnatal age, suggesting that inhibin is associated with a negative feedback signal for FSH in testicular maturation.
Figures
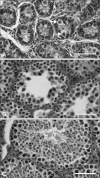
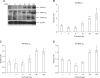
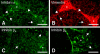
References
-
- Allenby G, Foster PM, Sharpe RM. Evidence that secretion of immunoactive inhibin by seminiferous tubules from the adult rat testis is regulated by specific germ cell types: correlation between in vivo and in vitro studies. Endocrinology. 1991;128:467–476. - PubMed
-
- Au CL, Robertson DM, de Kretser DM. Measurement of inhibin and an index of inhibin production by rat testes during postnatal development. Biol Reprod. 1986;35:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Buzzard JJ, Loveland KL, O'Bryan MK, O'Connor AE, Bakker M, Hayashi T, Wreford NG, Morrison JR, de Kretser DM. Changes in circulating and testicular levels of inhibin A and B and activin A during postnatal development in the rat. Endocrinology. 2004;145:3532–3541. - PubMed
-
- Clifton RJ, O'Donnell L, Robertson DM. Pachytene spermatocytes in co-culture inhibit rat Sertoli cell synthesis of inhibin βB-subunit and inhibin B but not the inhibin α-subunit. J Endocrinol. 2002;172:565–574. - PubMed
-
- de Kretser DM, Robertson DM. The isolation and physiology of inhibin and related proteins. Biol Reprod. 1989;40:33–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

