Current approaches to the treatment of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 19043519
- PMCID: PMC2536542
- DOI: 10.2147/ndt.s2006
Current approaches to the treatment of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Enormous progress has been made in the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD). As a result of advances in experimental therapeutics, many promising therapies for PD are emerging. Levodopa remains the most potent drug for controlling PD symptoms, yet is associated with significant complications such as the "wearing off" effect, levodopa-induced dyskinesias and other motor complications. Catechol-o-methyl-transferase inhibitors, dopamine agonists and nondopaminergic therapy are alternative modalities in the management of PD and may be used concomitantly with levodopa or one another. The neurosurgical treatment, focusing on deep brain stimulation, is reviewed briefly. Although this review has attempted to highlight the most recent advances in the treatment of PD, it is important to note that new treatments are not necessarily better than the established conventional therapy and that the treatment options must be individualized and tailored to the needs of each individual patient.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; deep brain stimulation; levodopa; medical treatment; pallidotomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
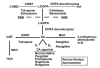
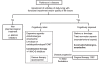
References
-
- Allain H, Cougnard J, Neukirch HC, et al. Selegilene in de novo parkinsonian patients: the French selegiline multicenter trial. Acta Neurol Scand. 1991;136:73–8. - PubMed
-
- Anderson VC, Burchiel KJ, Hogarth P, et al. Pallidal vs subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol. 2005;62:554–60. - PubMed
-
- Assal F, Spahr L, Hadengue A, et al. Tolcapone and fulminant hepatitis. Lancet. 1998;19:958. - PubMed
-
- Barone I, Rektor I, Bares M, et al. Pramipexole and pergolide in the treatment of depression in Parkinson’s disease: a national multicentre prospective randomized study. Eur J Neurol. 2003;10:399–406. - PubMed
-
- Baronti F, Davis TL, Boldry RC, et al. Deprenyl effects on levodopa pharmacodynamics, mood and free radical scavenging. Neurology. 1992;42:541–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

