Phenotypic and functional alterations of Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cell subsets in patients with active nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 19043708
- PMCID: PMC2695875
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-008-0629-8
Phenotypic and functional alterations of Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cell subsets in patients with active nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
Introduction: Human Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells play important role in immunity to infection and cancer by monitoring self and foreign isoprenoid metabolites with their gammadelta T cell antigen receptors. Like CD4 and CD8 alphabeta T cells, adult peripheral Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells represent a pool of heterogeneous cells with distinct functional capabilities.
Purpose: The aim of this study was to characterize the phenotypes and functions of various Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cell subsets in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). We sought to develop a better understanding of the role of these cells during the course of disease and to facilitate the development of immunotherapeutic strategies against NPC.
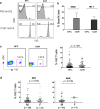
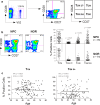
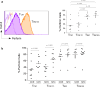
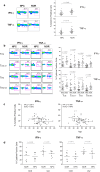
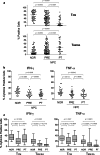
Results: Although similar total percentages of peripheral blood Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells were found in both NPC patients and normal donors, Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells from NPC patients showed decreased cytotoxicity against tumor cells whereas Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells from normal donors showed potent cytotoxicity. To investigate further, we compared the phenotypic characteristics of Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells from 96 patients with NPC and 54 healthy controls. The fraction of late effector memory Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells (T(EM RA)) was significantly increased in NPC patients with corresponding decreases in the fraction of early memory Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells (T(CM)) compared with those in healthy controls. Moreover, T(EM RA) and T(CM) Vgamma2Vdelta2 cells from NPC patients produced significantly less IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha, potentially contributing to their impaired cytotoxicity. Radiotherapy or concurrent chemo-radiotherapy further increased the T(EM RA) Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cell population but did not correct the impaired production of IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha observed for T(EM RA) Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells.
Conclusion: We have identified distinct alterations in the Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cell subsets of patients with NPC. Moreover, the overall cellular effector function of gammadelta T cells is compromised in these patients. Our data suggest that the contribution of Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells to control NPC may depend on the activation state and differentiation of these cells.
Figures
References
-
- Appay V, Dunbar PR, Callan M, Klenerman P, Gillespie GM, Papagno L, Ogg GS, King A, Lechner F, Spina CA, Little S, Havlir DV, Richman DD, Gruener N, Pape G, Waters A, Easterbrook P, Salio M, Cerundolo V, McMichael AJ, Rowland-Jones SL. Memory CD8+ T cells vary in differentiation phenotype in different persistent virus infections. Nat Med. 2002;8:379–385. doi: 10.1038/nm0402-379. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bennouna J, Bompas E, Neidhardt EM, Rolland F, Philip I, Galea C, Salot S, Saiagh S, Audrain M, Rimbert M, Lafaye-de Micheaux S, Tiollier J, Negrier S. Phase-I study of Innacell γδ™, an autologous cell-therapy product highly enriched in γ9δ2 T lymphocytes, in combination with IL-2, in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2008;57:1599–1609. doi: 10.1007/s00262-008-0491-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caccamo N, Battistini L, Bonneville M, Poccia F, Fournie JJ, Meraviglia S, Borsellino G, Kroczek RA, La Mendola C, Scotet E, Dieli F, Salerno A. CXCR5 identifies a subset of Vγ9 Vδ2 T cells which secrete IL-4 and IL-10 and help B cells for antibody production. J Immunol. 2006;177:5290–5295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

