Regulation of CART peptide expression by CREB in the rat nucleus accumbens in vivo
- PMID: 19046951
- PMCID: PMC2734444
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.11.011
Regulation of CART peptide expression by CREB in the rat nucleus accumbens in vivo
Abstract
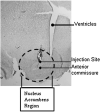
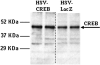
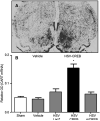
Production of mRNA from the cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) gene is regulated by cocaine and other drugs of abuse in the nucleus accumbens (NAc), a brain reward region. Current hypotheses postulate that CART peptides there oppose the rewarding actions of cocaine by opposing the effects of dopaminergic transmission. Since over expression of CREB was shown to decrease cocaine-mediated reward, we hypothesized that CART could be a target gene for CREB in the NAc and that over expression of CREB would increase CART peptide levels. Transcription factor (TF) binding to DNA is influenced by sequences adjacent to consensus TF binding sites and other factors. We thus examined CREB binding to a 27mer oligonucleotide containing the CRE sequence from the CART gene proximal promoter. Using electrophoretic mobility shift assays and TF-antibody super shift assays, CREB was found to bind to the CRE sequence from the CART promoter. To test if over expression of CREB in the NAc affected CART peptide levels, Herpes simplex virus-1 vectors over expressing CREB (HSV-CREB), or a vector that expressed LacZ (HSV-LacZ) as a control, were injected into the NAc of rats. Western blotting and in situ hybridization showed that HSV-CREB injections increased CART mRNA and peptide levels. Injections of a dominant negative CREB mutant (HSV-mCREB) did not alter either CART mRNA or peptide levels. The finding that CREB can regulate the levels of CART mRNA and peptides in vivo in the NAc supports a role for CART peptides in psychostimulant-induced reward and reinforcement.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays revealed CREB and serine 133 phospho-CREB binding to the CART gene proximal promoter.Brain Res. 2010 Jul 16;1344:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.04.069. Epub 2010 May 6. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20451507 Free PMC article.
-
Cocaine-amphetamine-regulated transcript expression in the rat nucleus accumbens is regulated by adenylyl cyclase and the cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate/protein kinase a second messenger system.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Apr;317(1):454-61. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.096123. Epub 2005 Dec 1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006. PMID: 16322355
-
Altered responsiveness to cocaine and increased immobility in the forced swim test associated with elevated cAMP response element-binding protein expression in nucleus accumbens.J Neurosci. 2001 Sep 15;21(18):7397-403. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-18-07397.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11549750 Free PMC article.
-
Reflections on: "A general role for adaptations in G-Proteins and the cyclic AMP system in mediating the chronic actions of morphine and cocaine on neuronal function".Brain Res. 2016 Aug 15;1645:71-4. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.12.039. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26740398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of CART in the reward/reinforcing properties of psychostimulants.Peptides. 2006 Aug;27(8):1993-2004. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2006.03.034. Peptides. 2006. PMID: 16766084 Review.
Cited by
-
Methamphetamine Induces TET1- and TET3-Dependent DNA Hydroxymethylation of Crh and Avp Genes in the Rat Nucleus Accumbens.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Jun;55(6):5154-5166. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0750-9. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28842817 Free PMC article.
-
CREB-Binding Protein Regulates Cocaine- and Amphetamine-Regulated Transcript Peptide Expression in the Lateral Hypothalamus: Implication in Reward and Reinforcement.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Feb;62(2):1388-1403. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04338-7. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 38987488
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays revealed CREB and serine 133 phospho-CREB binding to the CART gene proximal promoter.Brain Res. 2010 Jul 16;1344:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.04.069. Epub 2010 May 6. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20451507 Free PMC article.
-
Predominant D1 Receptors Involvement in the Over-expression of CART Peptides after Repeated Cocaine Administration.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Mar;19(2):89-97. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.2.89. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25729269 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture alleviates retrieval of pain memory and its effect on phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein in anterior cingulate cortex in rats.Behav Brain Funct. 2015 Mar 4;11:9. doi: 10.1186/s12993-015-0055-y. Behav Brain Funct. 2015. PMID: 25886521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrett P, Davidson J, Morgan P. CART gene promoter transcription is regulated by a cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element. Obes. Res. 2002;10:1291–1298. - PubMed
-
- Boonyaratanakornkit V, Melvin V, Prendergast P, Altmann M, Ronfani L, Bianchi ME, Taraseviciene L, Nordeen SK, Allegretto EA, Edwards DP. High-mobility group chromatin proteins 1 and 2 functionally interact with steroid hormone receptors to enhance their DNA binding in vitro and transcriptional activity in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998;18:4471–4487. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carlezon WA, Jr., Thome J, Olson VG, Lane-Ladd SB, Brodkin ES, Hiroi N, Duman RS, Neve RL, Nestler EJ. Regulation of cocaine reward by CREB. Science. 1998;282:2272–2275. - PubMed
-
- Carlezon WA, Jr., Nestler EJ, Neve RL. Herpes simplex virus-mediated gene transfer as a tool for neuropsychiatric research. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 2000;4(1):47–67. Review. - PubMed
-
- Carlezon WA, Jr., Duman RS, Nestler EJ. The many faces of CREB. Trends Neurosci. 2005;28:436–445. Review. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K05 DA000418/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA08227/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA015162/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA00418/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA000219/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA008227/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P51 RR000165/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH066172/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA015040/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 5F31DA0219/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA15162/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA015040/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RR00165/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

