In vivo expansion, persistence, and function of peptide vaccine-induced CD8 T cells occur independently of CD4 T cells
- PMID: 19047170
- PMCID: PMC2679655
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3134
In vivo expansion, persistence, and function of peptide vaccine-induced CD8 T cells occur independently of CD4 T cells
Abstract
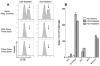
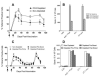
Significant efforts are being devoted toward the development of effective therapeutic vaccines against cancer. Specifically, well-characterized subunit vaccines, which are designed to generate antitumor cytotoxic CD8 T-cell responses. Because CD4 T cells participate at various stages of CD8 T-cell responses, it is important to study the role of CD4 T cells in the induction and persistence of antitumor CD8 T-cell responses by these vaccines. Recent evidence points to the requirement of CD4 T cells for the long-term persistence of memory CD8 T cells, which in the case of cancer immunotherapy would be critical for the prevention of tumor recurrences. The purpose of the present study was to assess whether CD4 T cells are necessary for the generation and maintenance of antigen-specific CD8 T cells induced by subunit (peptide or DNA) vaccines. We have used a vaccination strategy that combines synthetic peptides representing CD8 T-cell epitopes, a costimulatory anti-CD40 antibody and a Toll-like receptor agonist (TriVax) to generate large numbers of antigen-specific CD8 T-cell responses. Our results show that the rate of decline (clonal contraction) of the antigen-specific CD8 T cells and their functional state is not affected by the presence or absence of CD4 T cells throughout the immune response generated by TriVax. We believe that these results bear importance for the design of effective vaccination strategies against cancer.
Figures

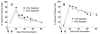


References
-
- Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F. Understanding the generation and function of memory T cell subsets. Current Opin Immunol. 2005;17:326–32. - PubMed
-
- Prlic M, Williams MA, Bevan MJ. Requirements for CD8 T-cell priming, memory generation and maintenance. Current Opin Immunol. 2007;19:315–9. - PubMed
-
- Antia R, Ganusov VV, Ahmed R. The role of models in understanding CD8+ T-cell memory. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:101–11. - PubMed
-
- Bennett SR, Carbone FR, Karamalis F, Flavell RA, Miller JF, Heath WR. Help for cytotoxic-T-cell responses is mediated by CD40 signalling. Nature. 1998;393:478–80. - PubMed
-
- Ridge JP, Di Rosa F, Matzinger P. A conditioned dendritic cell can be a temporal bridge between a CD4+ T-helper and a T-killer cell. Nature. 1998;393:474–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

