The Brucella abortus S19 DeltavjbR live vaccine candidate is safer than S19 and confers protection against wild-type challenge in BALB/c mice when delivered in a sustained-release vehicle
- PMID: 19047401
- PMCID: PMC2632017
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01017-08
The Brucella abortus S19 DeltavjbR live vaccine candidate is safer than S19 and confers protection against wild-type challenge in BALB/c mice when delivered in a sustained-release vehicle
Abstract
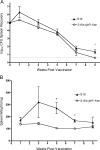
Brucellosis is an important zoonotic disease of nearly worldwide distribution. Despite the availability of live vaccine strains for bovine (S19, RB51) and small ruminants (Rev-1), these vaccines have several drawbacks, including residual virulence for animals and humans. Safe and efficacious immunization systems are therefore needed to overcome these disadvantages. A vjbR knockout was generated in the S19 vaccine and investigated for its potential use as an improved vaccine candidate. Vaccination with a sustained-release vehicle to enhance vaccination efficacy was evaluated utilizing the live S19 DeltavjbR::Kan in encapsulated alginate microspheres containing a nonimmunogenic eggshell precursor protein of the parasite Fasciola hepatica (vitelline protein B). BALB/c mice were immunized intraperitoneally with either encapsulated or nonencapsulated S19 DeltavjbR::Kan at a dose of 1 x 10(5) CFU per animal to evaluate immunogenicity, safety, and protective efficacy. Humoral responses postvaccination indicate that the vaccine candidate was able to elicit an anti-Brucella-specific immunoglobulin G response even when the vaccine was administered in an encapsulated format. The safety was revealed by the absence of splenomegaly in mice that were inoculated with the mutant. Finally, a single dose with the encapsulated mutant conferred higher levels of protection compared to the nonencapsulated vaccine. These results suggest that S19 DeltavjbR::Kan is safer than S19, induces protection in mice, and should be considered as a vaccine candidate when administered in a sustained-release manner.
Figures



References
-
- Abraham, S. M., R. F. Vieth, and D. J. Burgess. 1996. Novel technology for the preparation of sterile alginate-poly-l-lysine microcapsules in a bioreactor. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 163-68. - PubMed
-
- Allsup, T. N. 1969. Abortion in sheep associated with Brucella abortus infection. Vet. Rec. 84104-108. - PubMed
-
- Boschiroli, M. L., V. Foulongne, and D. O'Callaghan. 2001. Brucellosis: a worldwide zoonosis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 458-64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

