uPA modulates the age-dependent effect of brain injury on cerebral hemodynamics through LRP and ERK MAPK
- PMID: 19050721
- PMCID: PMC3538352
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2008.142
uPA modulates the age-dependent effect of brain injury on cerebral hemodynamics through LRP and ERK MAPK
Abstract
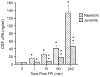
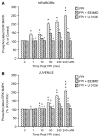
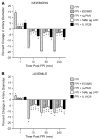
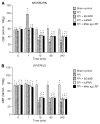
We hypothesized that urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) contributes to age-dependent early hyperemia after fluid percussion brain injury (FPI) by activating extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), leading to histopathologic changes in the underlying cortex. Both cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) uPA and phosphorylation of CSF ERK MAPK was increased at 1 min after FPI in newborn pigs, but was unchanged in juvenile pigs. uPA and phosphorylated ERK MAPK, detectable in sham piglet brain by immunohistochemistry, was markedly elevated and associated with histopathology 4 h after FPI in the newborn but there was minimal staining and histopathology in the juvenile. EEIIMD, a peptide derived from PA inhibitor-1 that does not affect proteolysis, blunted FPI-induced phosphorylation of ERK MAPK. FPI produced pial artery dilation and increased cerebral blood flow at 1 min after insult in the newborn, but not in the juvenile. Antilipoprotein-related protein (LRP) antibody, EEIIMD, a soluble uPA antagonist, and the ERK MAPK antagonist U 0126 inhibited FPI-associated hyperemia. These data indicate that uPA is upregulated after FPI and produces an age-dependent early hyperemia followed by histopathology through an LRP- and ERK MAPK-dependent pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no duality of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Adelson PD, Clyde B, Kochanek PM, Wisniewski SR, Marion DW, Yonas H. Cerebrovascular response in infants and young children following severe traumatic brain injury: a preliminary report. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1997a;26:200–7. - PubMed
-
- Adelson PD, Dixon CE, Robichaud P, Kochanek PM. Motor and cognitive functional deficits following diffuse traumatic brain injury in the immature rat. J Neurotrauma. 1997b;14:99–108. - PubMed
-
- Akkawi S, Nassar T, Tarshis M, Cines DB, Higazi AAR. LRP and avB3 mediate tPA-activation of smooth muscle cells. AJP. 2006;291:H1351–9. - PubMed
-
- Armstead WM. NOC/oFQ contributes to age dependent impairment of NMDA induced cerebrovasodilation after brain injury. Am J Physiol. 2000;279:H2188–95. - PubMed
-
- Armstead WM. PTK, ERK, and p38 MAPK contribute to impaired NMDA vasodilation after brain injury. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;474:249–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA083121/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL76206/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HD57355/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL076406/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076206/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NS53410/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- CA83121/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL81864/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007971/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD057355/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HL82545/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS053410/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077760/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL76406/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL77760/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL081864/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL07971/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

