A 15q13.3 microdeletion segregating with autism
- PMID: 19050728
- PMCID: PMC2986268
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2008.228
A 15q13.3 microdeletion segregating with autism
Abstract
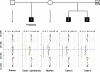
Autism and mental retardation (MR) show high rates of comorbidity and potentially share genetic risk factors. In this study, a rare approximately 2 Mb microdeletion involving chromosome band 15q13.3 was detected in a multiplex autism family. This genomic loss lies between distal break points of the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome locus and was first described in association with MR and epilepsy. Together with recent studies that have also implicated this genomic imbalance in schizophrenia, our data indicate that this CNV shows considerable phenotypic variability. Further studies should aim to characterise the precise phenotypic range of this CNV and may lead to the discovery of genetic or environmental modifiers.
Figures

References
-
- Bailey A, Le Couteur A, Gottesman I, et al. Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: evidence from a British twin study. Psychol Med. 1995;25:63–77. - PubMed
-
- Steyaert JG, De La Marche W. What's new in autism. Eur J Pediatr. 2008;167:1091–1101. - PubMed
-
- Sykes NH, Lamb JA. Autism: the quest for the genes. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2007;9:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Baker P, Piven J, Schwartz S, Patil S. Brief report: duplication of chromosome 15q11-13 in two individuals with autistic disorder. J Autism Dev Disord. 1994;24:529–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

